- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
How should emergency situations such as sewage pump failure or system overflow be managed?
Managing emergency situations such as sewage pump failure or system overflow requires a proactive approach that includes preparation, immediate response, and effective recovery. Here are the steps to handle these emergencies:
Emergency Plan: Develop a comprehensive emergency response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a pump failure or overflow. Ensure all relevant personnel are familiar with the plan.
Training: Conduct regular training sessions for staff to ensure they know how to respond to emergencies. This includes operating backup systems, using emergency equipment, and following safety protocols.
Backup Systems: Install backup pumps and power supplies to ensure continued operation during a primary pump failure or power outage. Regularly test these backups to ensure they are operational.
Alarms and Monitoring: Install alarm systems and remote monitoring to provide early warning of pump failure or high-water levels. Ensure these systems are regularly tested and maintained.
Preventive Maintenance: Implement a robust preventive maintenance program to reduce the likelihood of pump failures. Regularly inspect and maintain pumps, control panels, and other system components.
Immediate Response
Safety First: Ensure the safety of personnel by following all safety protocols. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and avoid contact with sewage.
Stop the Source: If possible, stop the flow of sewage into the system to prevent further overflow. This might involve shutting off water supply or redirecting flow to backup systems.

Activate Backup: Immediately activate backup pumps or systems to restore sewage handling capacity. Ensure the transition to backup systems is smooth and that they are functioning correctly.
Contain the Overflow: Use barriers, absorbent materials, and containment strategies to prevent the spread of sewage. This can help minimize damage and contamination.
Notify Authorities: Notify local authorities, health departments, and regulatory agencies as required. Provide them with all necessary information about the situation and actions being taken.
Recovery
Cleanup: Initiate a thorough cleanup of the affected area once the immediate emergency is under control. This includes removing sewage, disinfecting surfaces, and ensuring proper disposal of contaminated materials.
Inspection and Repair: Conduct a detailed inspection of the sewage pump system to identify the cause of the failure or overflow. Repair or replace damaged components as needed.
Assessment: Assess the impact of the overflow on the surrounding environment and take necessary remediation actions to prevent environmental contamination.
Documentation: Document the incident, including the cause, response actions, and outcomes. This information is vital for future reference and improving emergency response plans.
Post-Incident Review and Improvement
Review: Conduct a post-incident review to evaluate the effectiveness of the response. Identify any weaknesses in the emergency plan and areas for improvement.
Update Plans: Update emergency response plans and procedures based on lessons learned from the incident. Ensure all relevant personnel are informed of any changes.
Training and Drills: Schedule additional training and emergency drills to reinforce new procedures and ensure preparedness for future incidents.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively manage emergency situations involving sewage pump failures or system overflows, minimizing the impact on operations and the environment while ensuring the safety of personnel.
Related Products
-
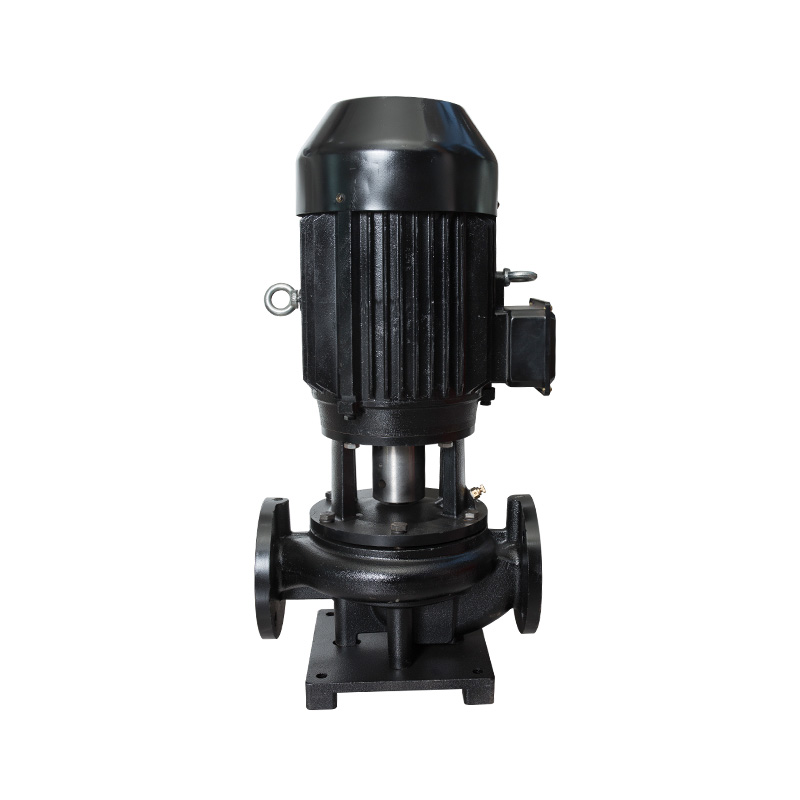

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
The TD type single-stage pipeline circulation pump is a green, environ...
See Details -
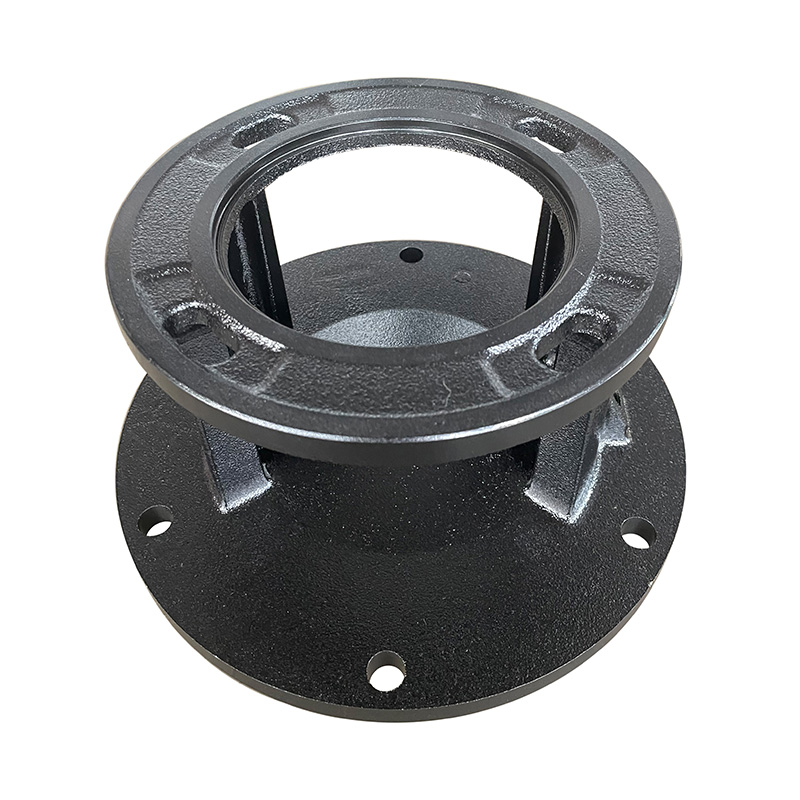

TD high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump vertical base
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
A vertical base is a pedestal used to support and secure a vertical TD...
See Details -

Horizontal pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISW series single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps ar...
See Details -
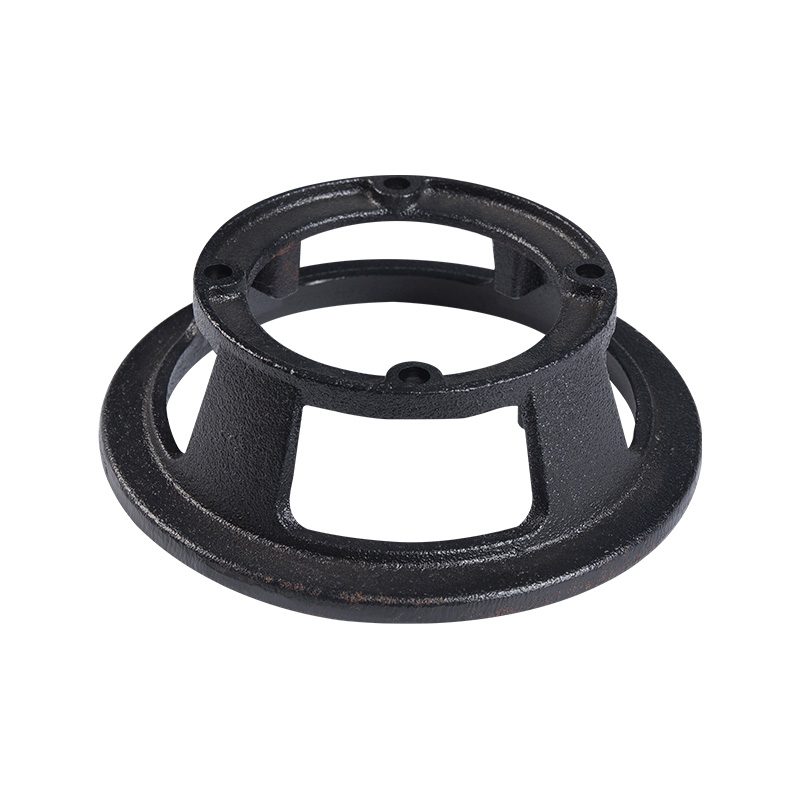

Sewage pump foot plate
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Components mounted on the bottom of the sewage pump unit to support th...
See Details -
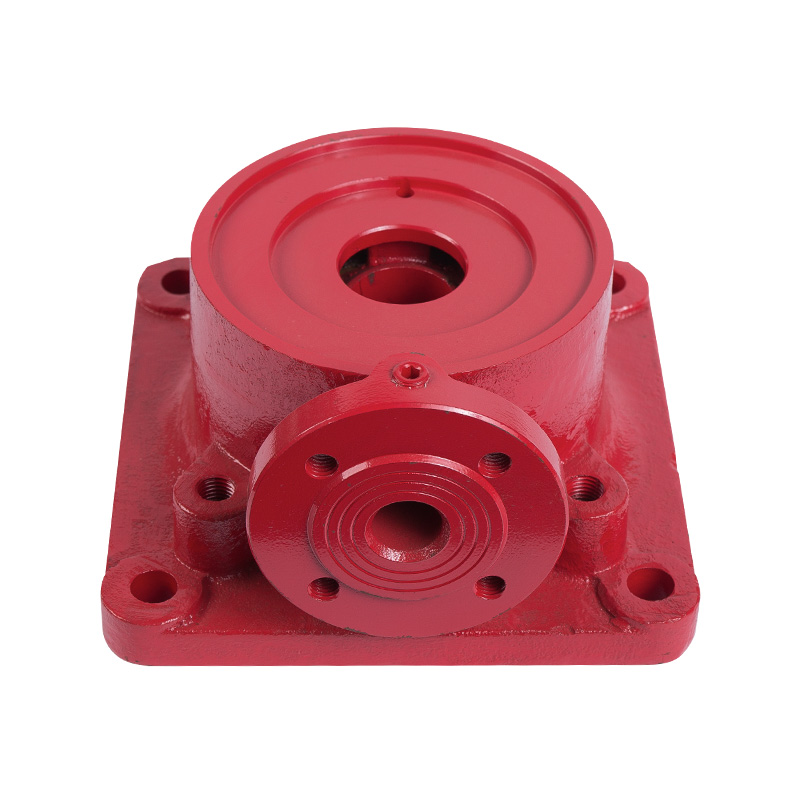

LG multi-stage pump water inlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The inlet section is the inlet portion of the pump and is responsible ...
See Details -
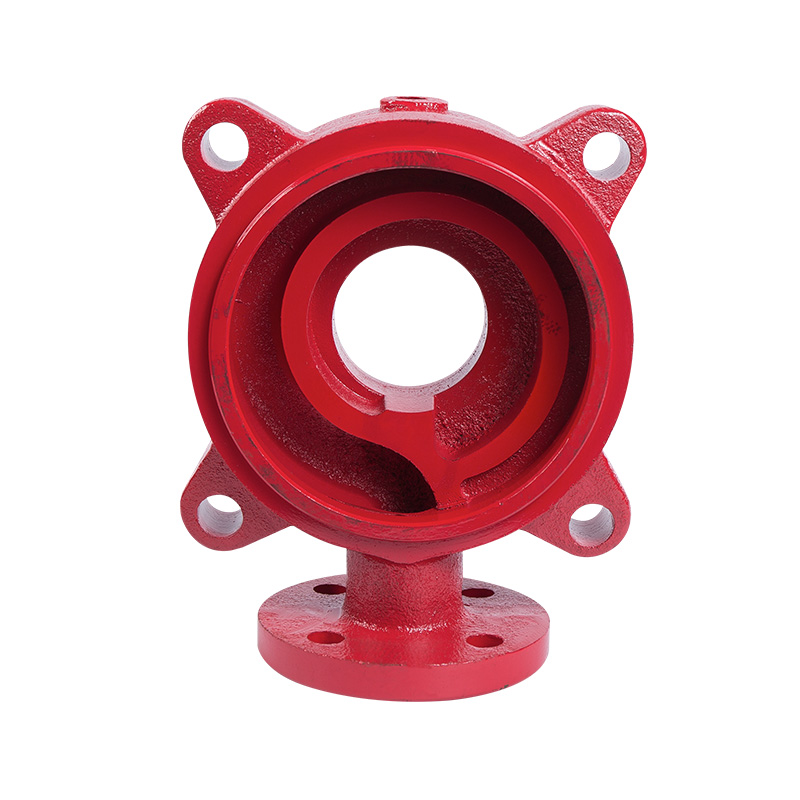

LG multi-stage pump water outlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The outlet section is the outlet part of the pump, which is responsibl...
See Details -
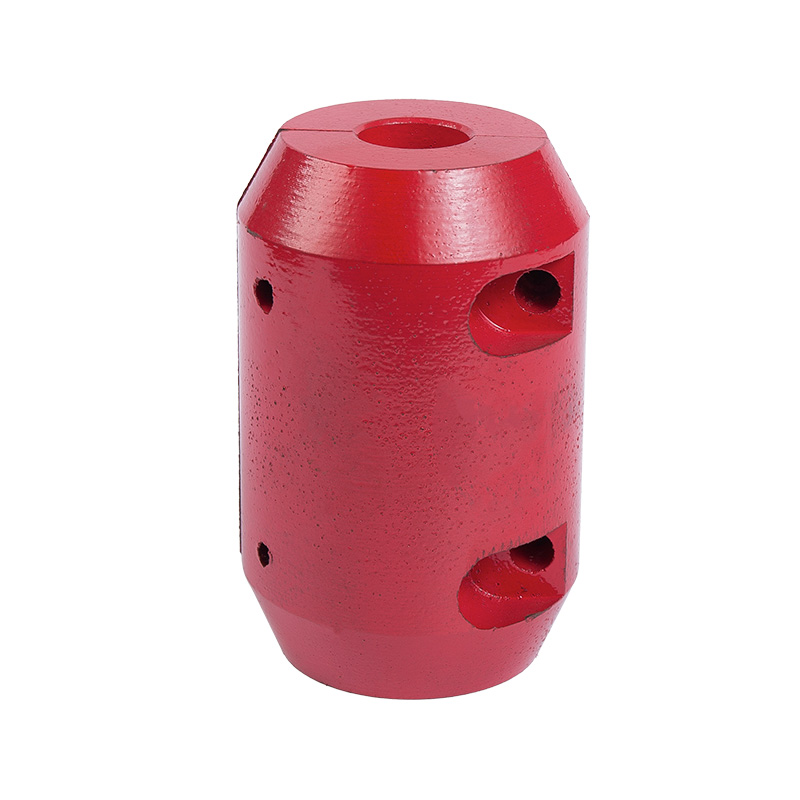

LG multi-stage pump coupling
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Couplings are used to connect the pump shaft to the motor shaft for en...
See Details -
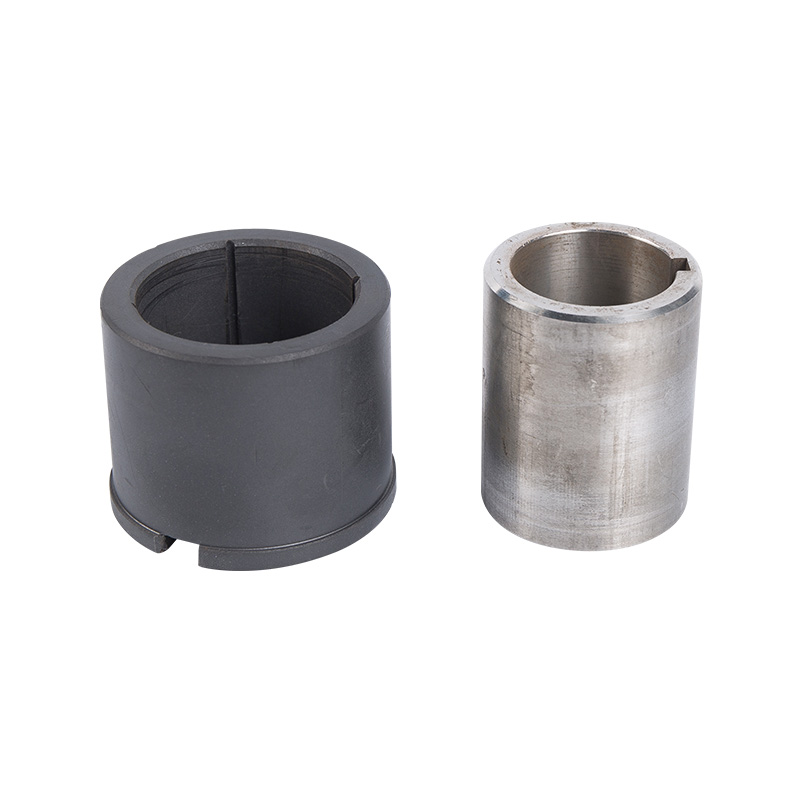

Stainless steel LG multi-stage pump bearing sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless Steel Bearing Sleeves are bearing sleeves made of stainless ...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump water bearing gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearing gland is the gland for fixing the water bearing, which s...
See Details -
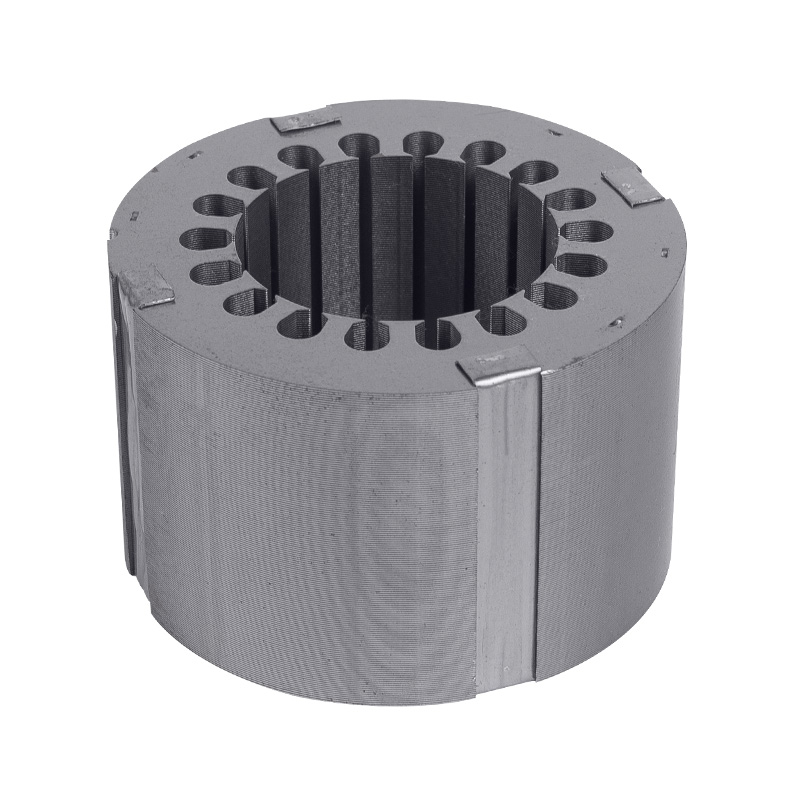

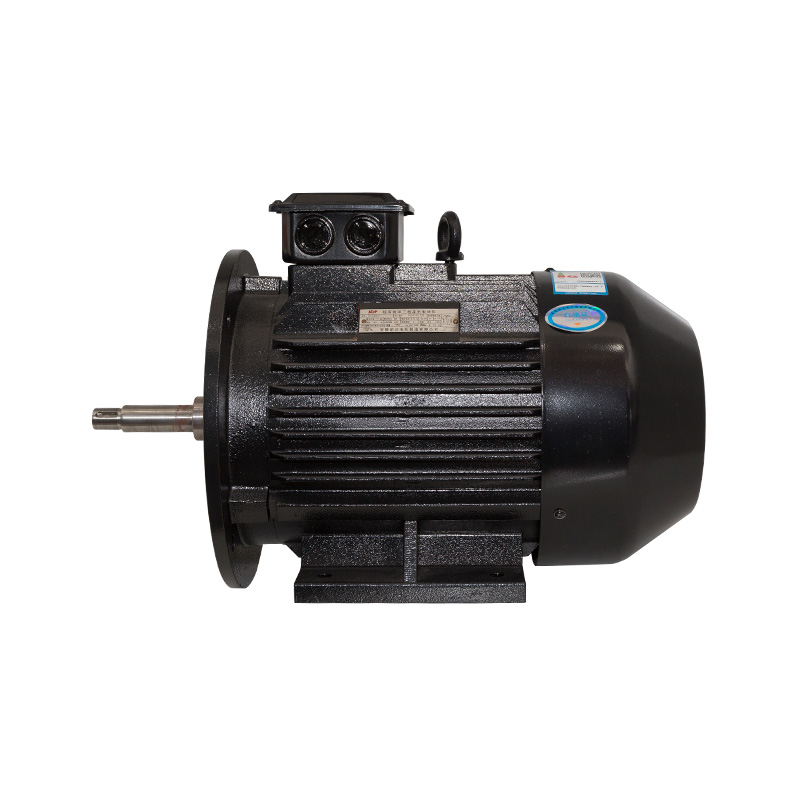
Motor core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A common motor structure, the stator is fixed by the iron core structu...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

