- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
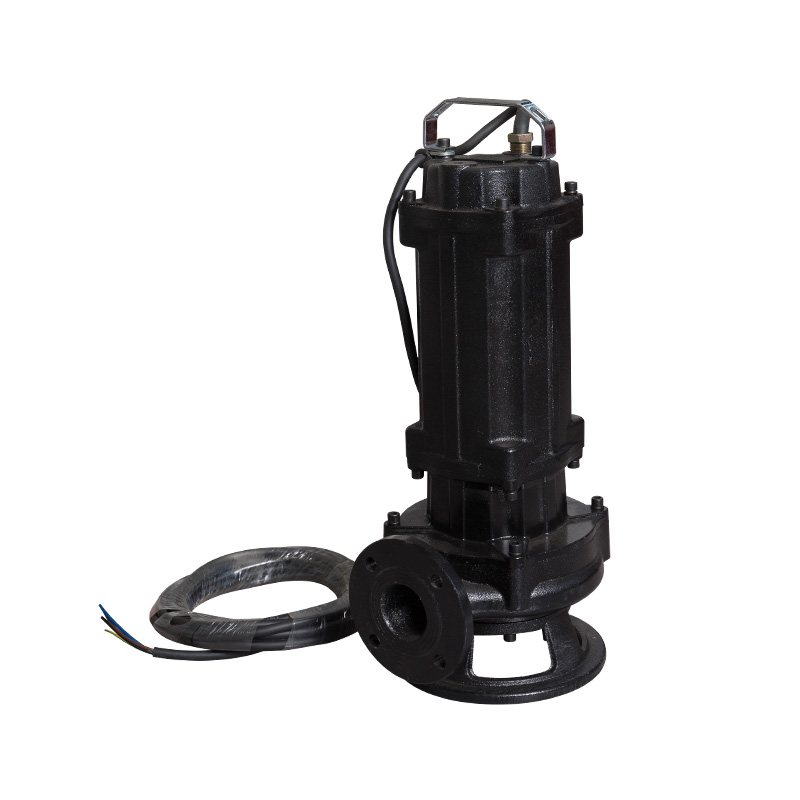
What are the best practices for installing sewage pumps to ensure optimal performance and longevity?
Best practices for installing sewage pumps to ensure optimal performance and longevity include careful planning, proper installation techniques, and ongoing maintenance. Here are some key guidelines:
Planning and Design
Assessment of Requirements: Conduct a thorough assessment of the building's sewage needs, including peak flow rates and head requirements.
Pump Selection: Choose the appropriate type of sewage pump (e.g., submersible, grinder, ejector) based on the specific application and sewage characteristics.
System Design: Design the system to minimize the risk of blockages and ensure smooth flow. This includes proper sizing of pipes and fittings.
Installation Techniques
Proper Sizing and Positioning: Ensure that the pump and associated components are correctly sized and positioned. The pump should be installed at a depth where it can effectively handle the sewage without being exposed to air.
Secure Mounting: Mount the pump securely to prevent movement and vibration, which can cause damage and reduce efficiency.
Correct Piping: Use the correct type and size of piping, and ensure that all connections are leak-free. Avoid sharp bends and sudden changes in pipe diameter to reduce the risk of blockages.
Ventilation: Install proper venting to prevent the buildup of gases and ensure smooth operation.
Check Valves: Install check valves to prevent backflow and reduce the risk of pump damage and system overflow.
Electrical Connections: Ensure that electrical connections are made by a qualified electrician and comply with local codes and regulations. Use waterproof connectors and properly rated circuits.
Safety Measures
Access for Maintenance: Design the installation to allow easy access for maintenance and inspection. This includes placing the pump in a location where it can be easily reached.
Alarm Systems: Install alarm systems to alert users to pump failures or high-water levels. Consider remote monitoring options for critical applications.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular Inspection: Schedule regular inspections to check for signs of wear, leaks, and other issues. Inspect the impeller, seals, and other critical components.
Cleaning: Regularly clean the pump and associated piping to remove debris and prevent blockages. This includes the use of backflushing if necessary.
Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated according to the manufacturer's recommendations.

Documentation and Training
Documentation: Keep detailed records of the installation, including diagrams, specifications, and maintenance logs. This information is crucial for troubleshooting and future maintenance.
Training: Provide training for staff on the operation and maintenance of the sewage pump system. This includes emergency procedures for pump failure or overflow situations.
Environmental Considerations
Protection from Contaminants: Ensure that the installation protects the pump and system from contaminants that could cause damage or reduce efficiency.
Flood Protection: If the pump is installed in a flood-prone area, take measures to protect it from flooding, such as elevated installation or waterproof enclosures.
Following these best practices can help ensure that a sewage pump system operates efficiently and reliably for many years, reducing the risk of failures and costly repairs.
Related Products
-
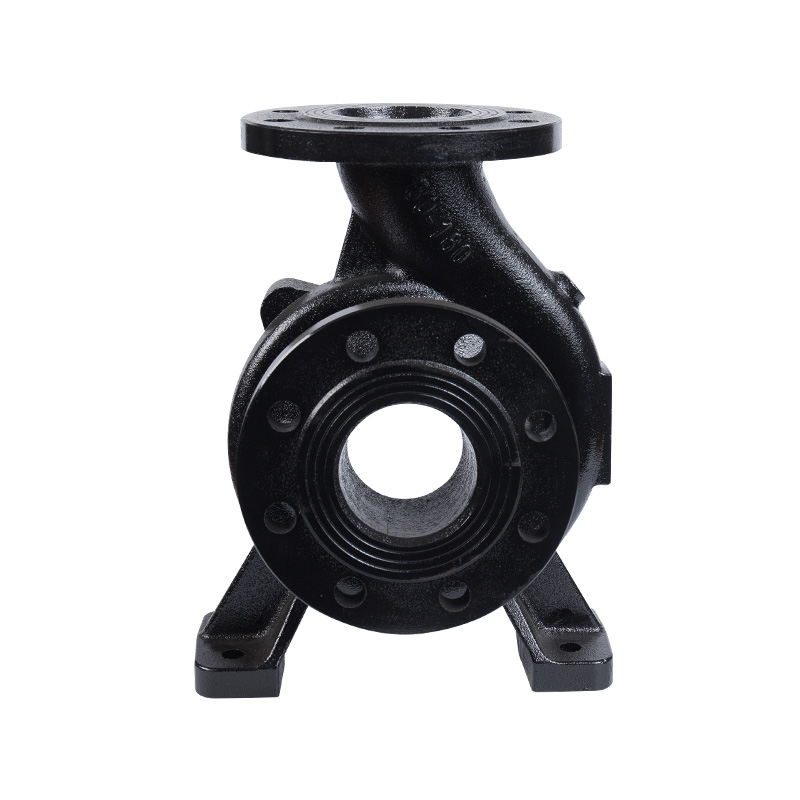

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
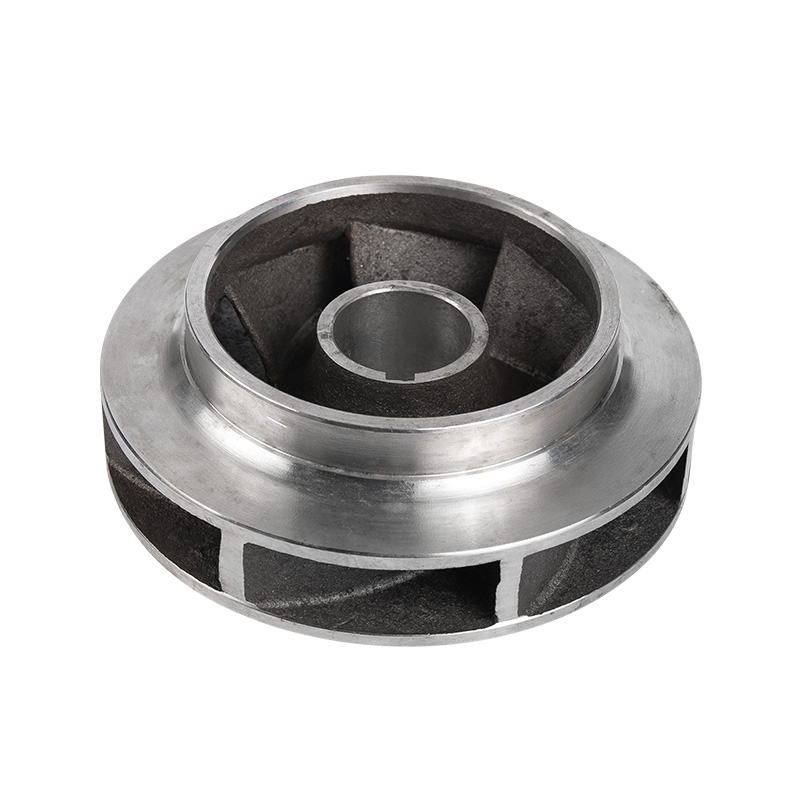

Pipe pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impeller material is stainless steel, it is not easy t...
See Details -
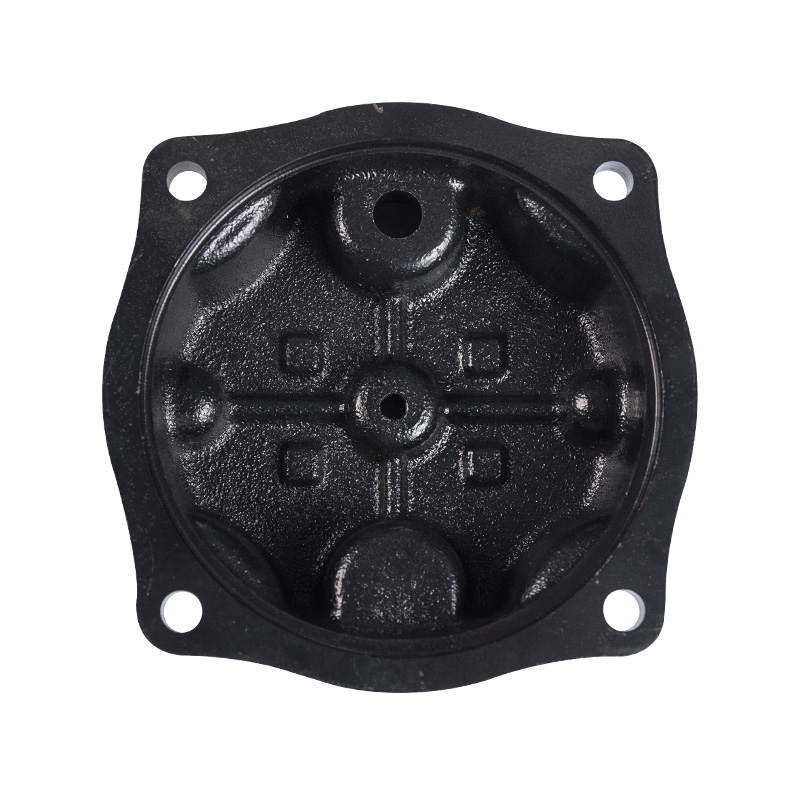

Sewage pump hanging cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the upper part of the sewage pump unit, it is used for li...
See Details -
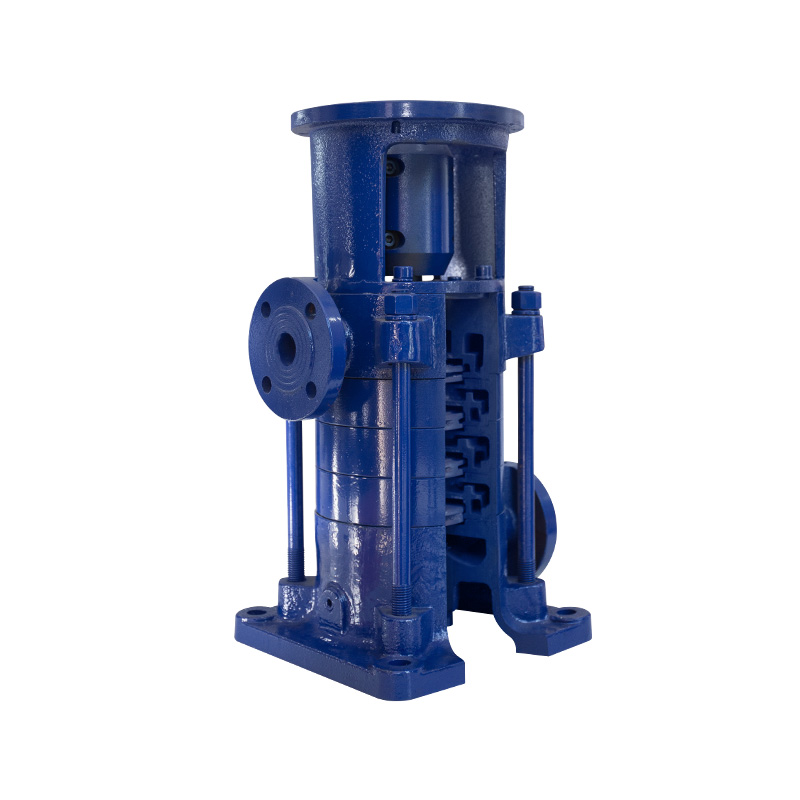

LG multistage pump 100 series
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump
Product features 1. Compact structure, small volume, small footprint. ...
See Details -
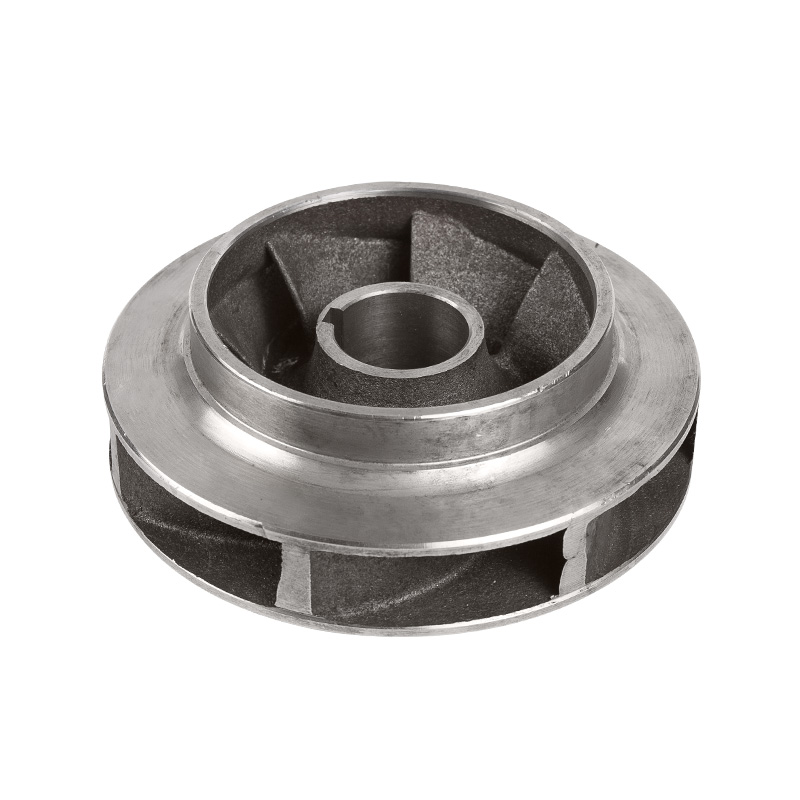

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
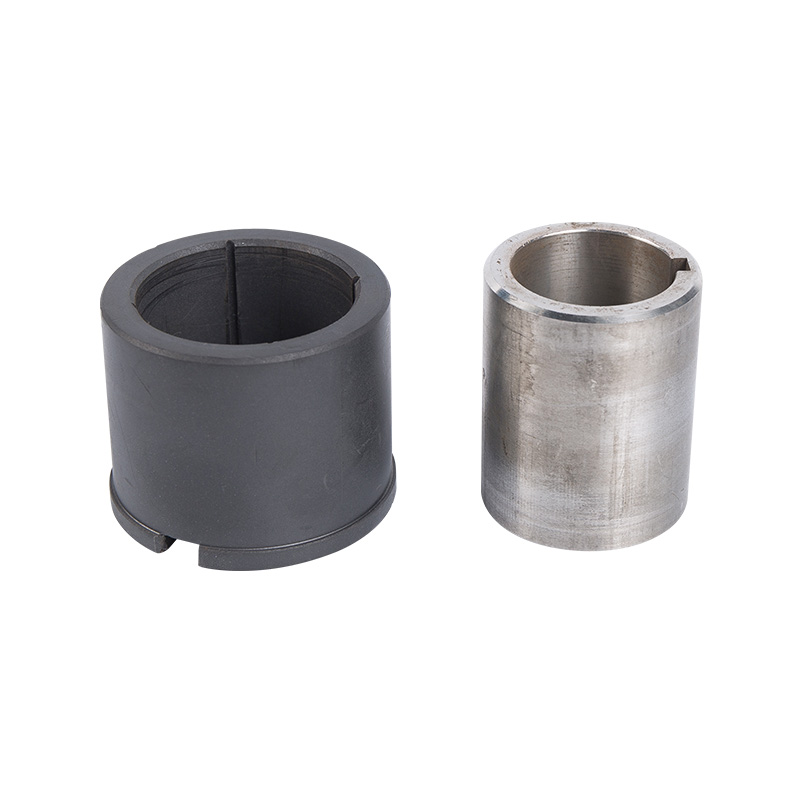

Stainless steel LG multi-stage pump bearing sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless Steel Bearing Sleeves are bearing sleeves made of stainless ...
See Details -
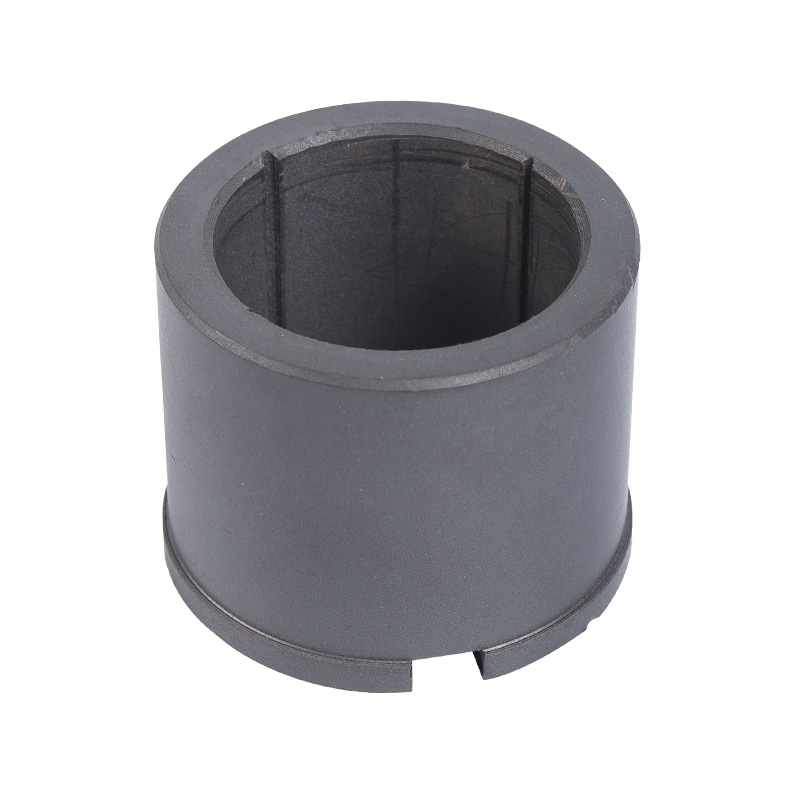

LG multi-stage pump water bearing
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearings are a special type of bearings commonly used in multi-s...
See Details -
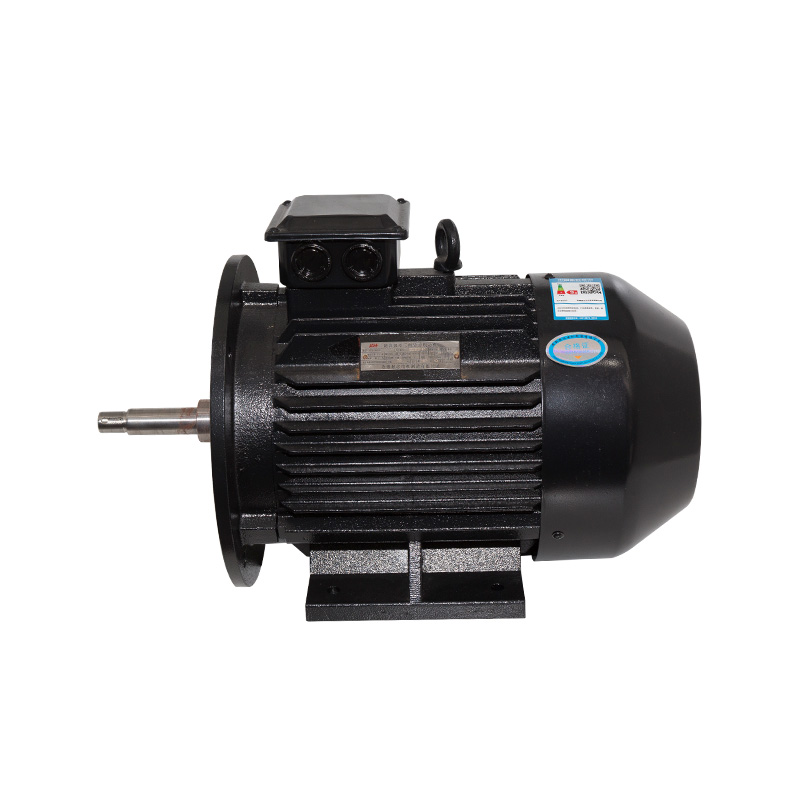

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
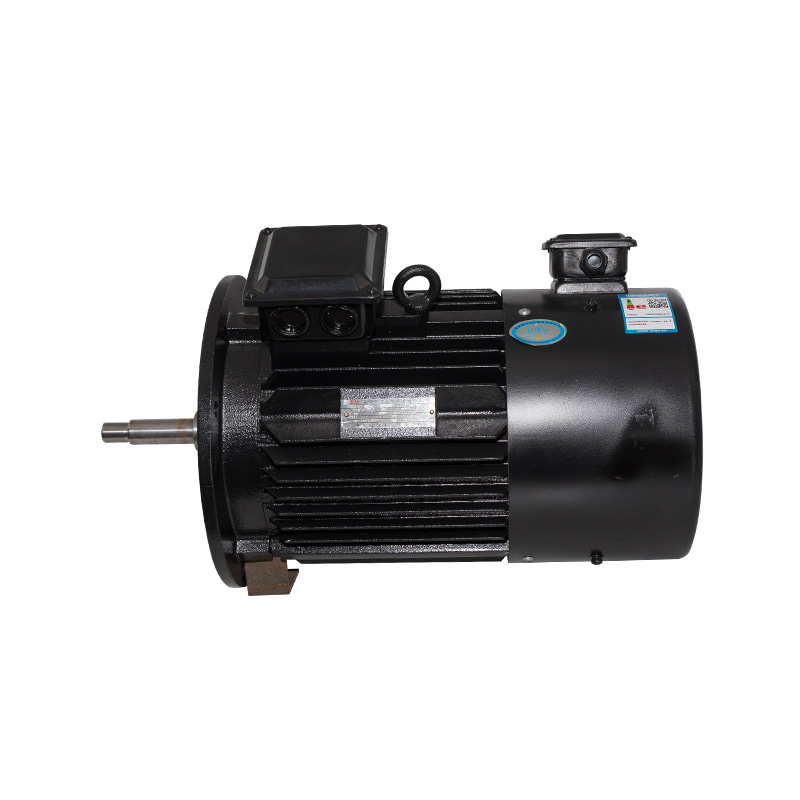

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details -
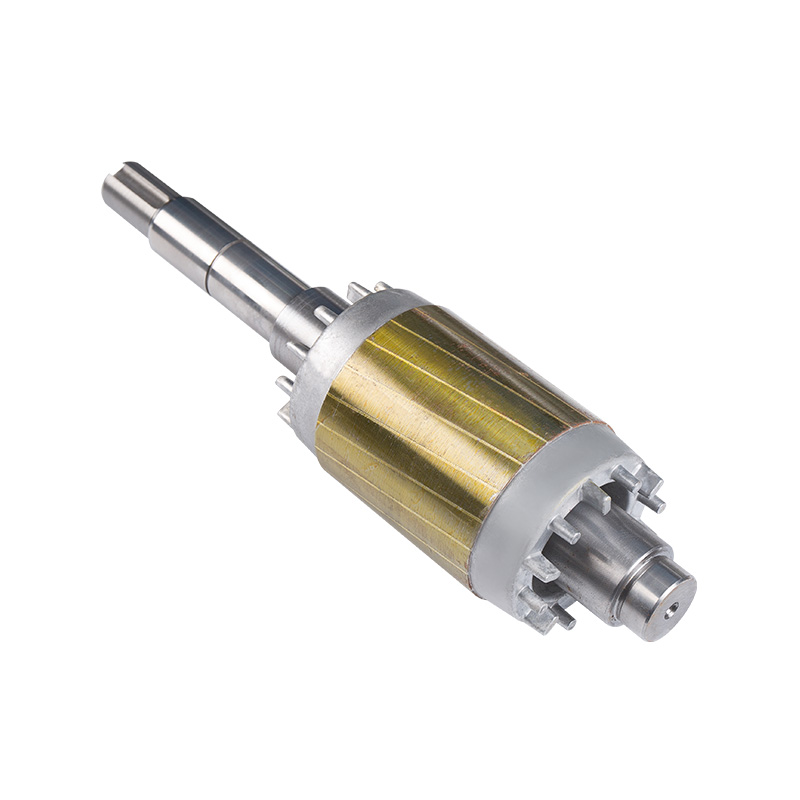

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

