- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What materials are commonly used in motor construction?
Electric motors are constructed from a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties that contribute to the motor's performance, efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the commonly used materials in motor construction and their roles:
Key Components and Materials:
Stator and Rotor:
Steel and Silicon Steel: The stator and rotor cores are typically made from laminated steel or silicon steel to reduce eddy current losses and improve magnetic properties. Silicon steel is preferred for its high permeability and low hysteresis loss.
Copper: Copper is commonly used for the windings in both the stator and rotor due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which helps reduce resistive losses and improve efficiency.
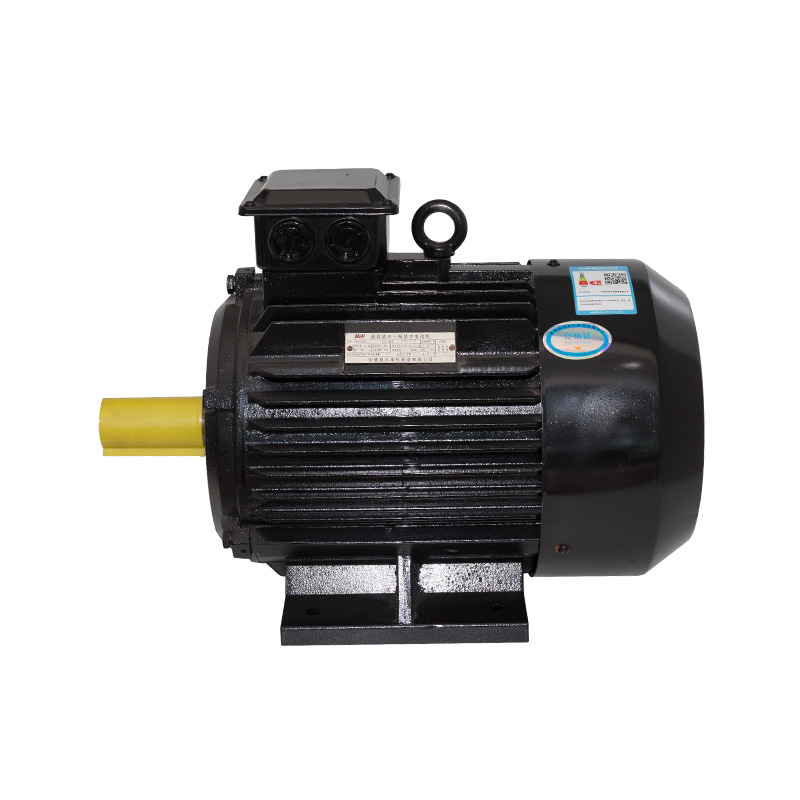

Aluminum: In some motors, especially smaller or lower-cost ones, aluminum is used for the rotor bars in induction motors due to its lower cost and adequate conductivity.
Windings:
Copper Wire: The windings are typically made from insulated copper wire. Copper is chosen for its high conductivity and flexibility, which helps in forming the coils and ensuring efficient current flow.
Insulation Materials: Various insulation materials are used to prevent short circuits and protect the windings from heat and mechanical stress. Common insulation materials include enamel coatings, varnishes, and insulating tapes made from materials like polyester or polyimide.
Bearings:
Steel Bearings: Bearings are usually made from high-grade steel for their strength and durability. They support the rotor and allow it to spin smoothly with minimal friction.
Ceramic Bearings: In some high-performance or specialized motors, ceramic bearings are used for their reduced friction, higher speed capabilities, and longer lifespan.
Housing and Frame:
Cast Iron: Cast iron is often used for motor housings and frames in industrial applications due to its strength, durability, and ability to dampen vibrations.
Aluminum: Aluminum is used for its lightweight and good thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice for the housing of smaller or portable motors.
Shaft:
Steel: The motor shaft is typically made from high-strength steel to transmit the rotational force from the motor to the load effectively. It needs to withstand high torsional stresses and wear.
Magnets:
Rare Earth Magnets: In permanent magnet motors, such as brushless DC motors, rare earth magnets like neodymium (NdFeB) are used for their strong magnetic fields and compact size.
Ferrite Magnets: Ferrite magnets are used in lower-cost applications where the magnetic field strength and efficiency are less critical.
Cooling Systems:
Fans and Fins: External cooling fans and fins made from aluminum or plastic are used to dissipate heat generated during motor operation.
Liquid Cooling Systems: In high-power motors, liquid cooling systems may be used, involving materials like copper or aluminum for heat exchangers and coolant pathways.
Commutator and Brushes (in brushed motors):
Copper: The commutator segments are often made from copper for good electrical conductivity.
Carbon/Graphite: Brushes are typically made from carbon or graphite to provide good electrical contact and wear resistance while maintaining low friction with the commutator.
Additional Materials:
Insulation and Potting Compounds:
Epoxy Resins: Used for potting and encapsulating components to protect against moisture, dust, and vibrations.
Thermal Interface Materials: Used to enhance heat transfer from the windings and other heat-generating components to the housing or cooling systems.
Fasteners and Connectors:
Steel or Stainless Steel: Used for bolts, screws, and other fasteners to ensure structural integrity.
Copper or Brass: Used for electrical connectors and terminals for their conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
These materials are chosen based on their specific properties and the requirements of the motor's application. The combination of these materials in various components ensures that electric motors are efficient, durable, and capable of performing their intended functions reliably.
Related Products
-
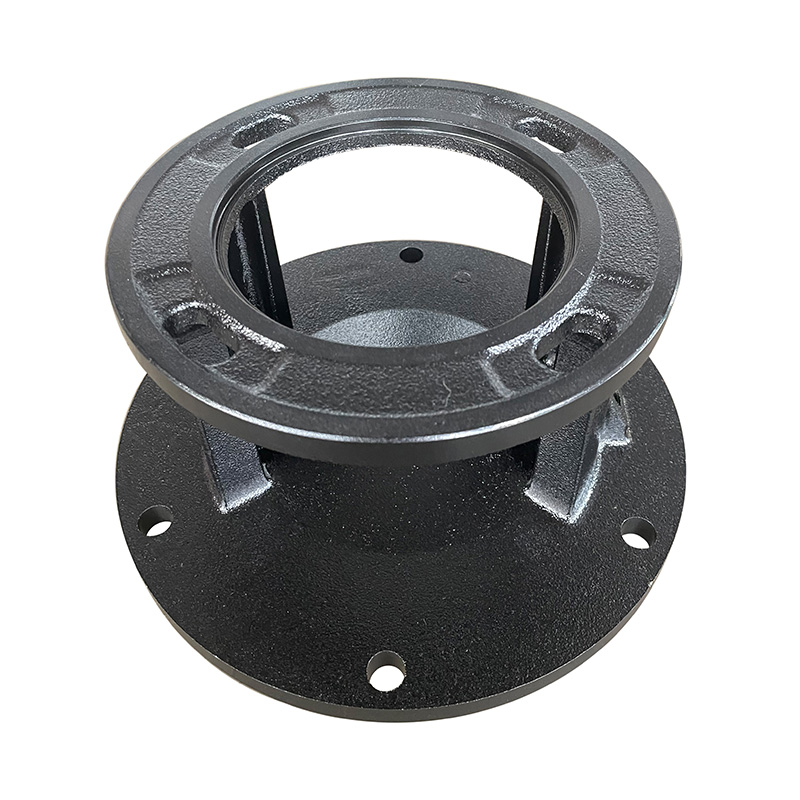

TD high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump vertical base
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
A vertical base is a pedestal used to support and secure a vertical TD...
See Details -
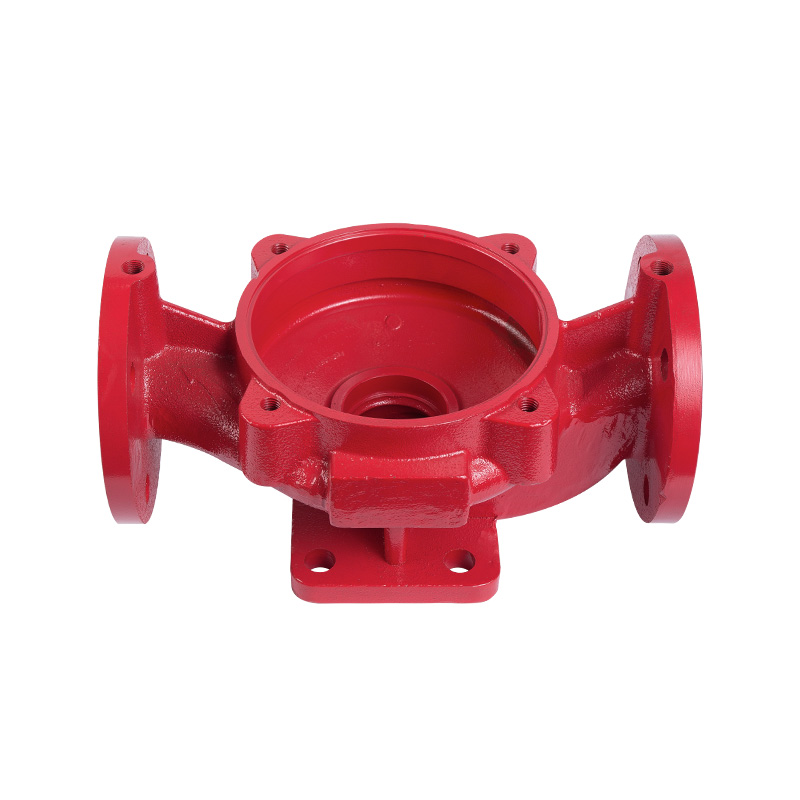

Vertical pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
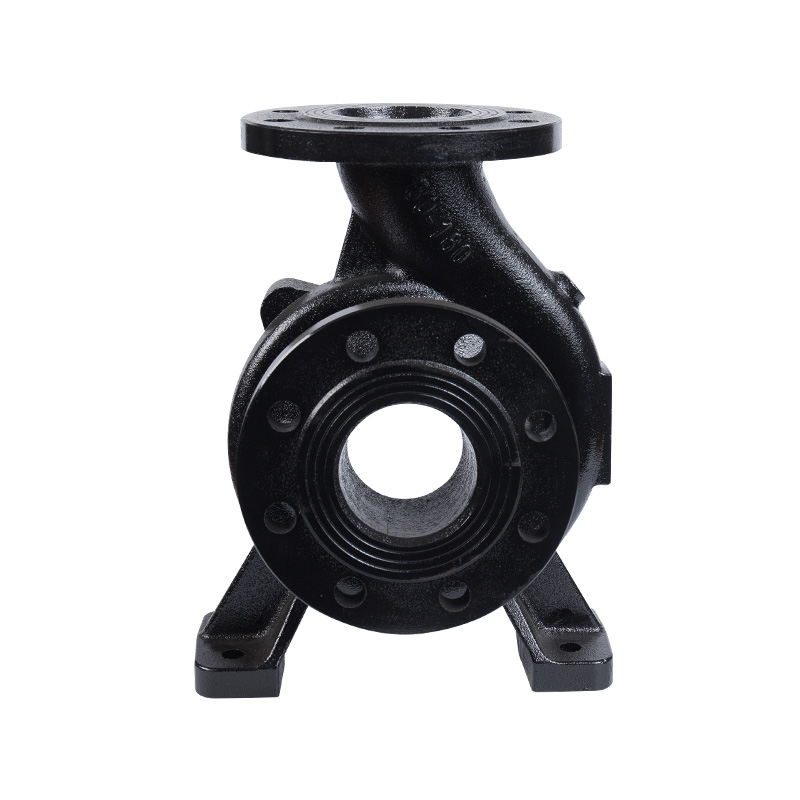

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
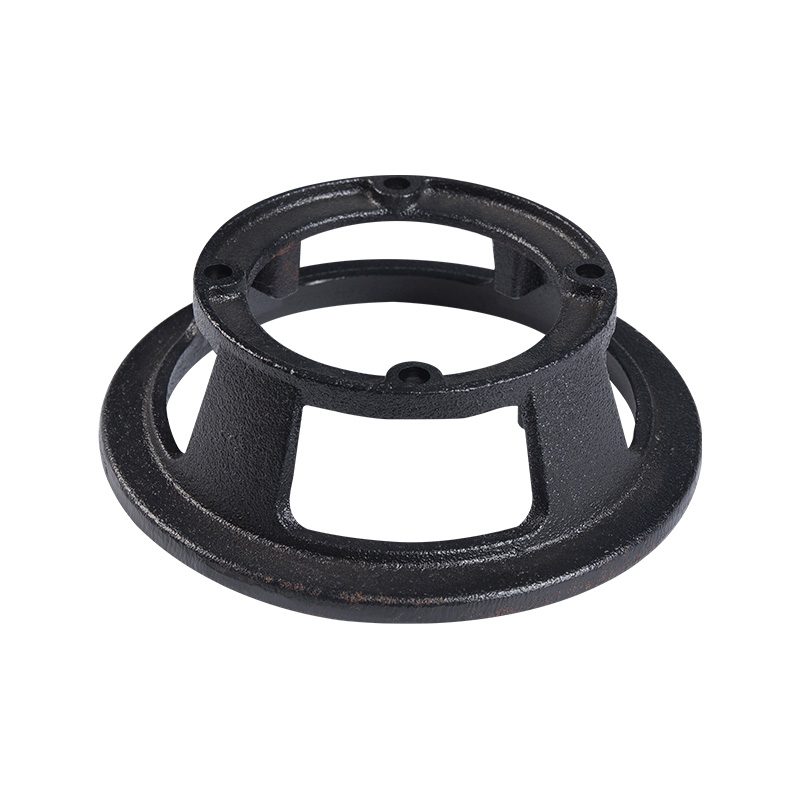

Sewage pump foot plate
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Components mounted on the bottom of the sewage pump unit to support th...
See Details -
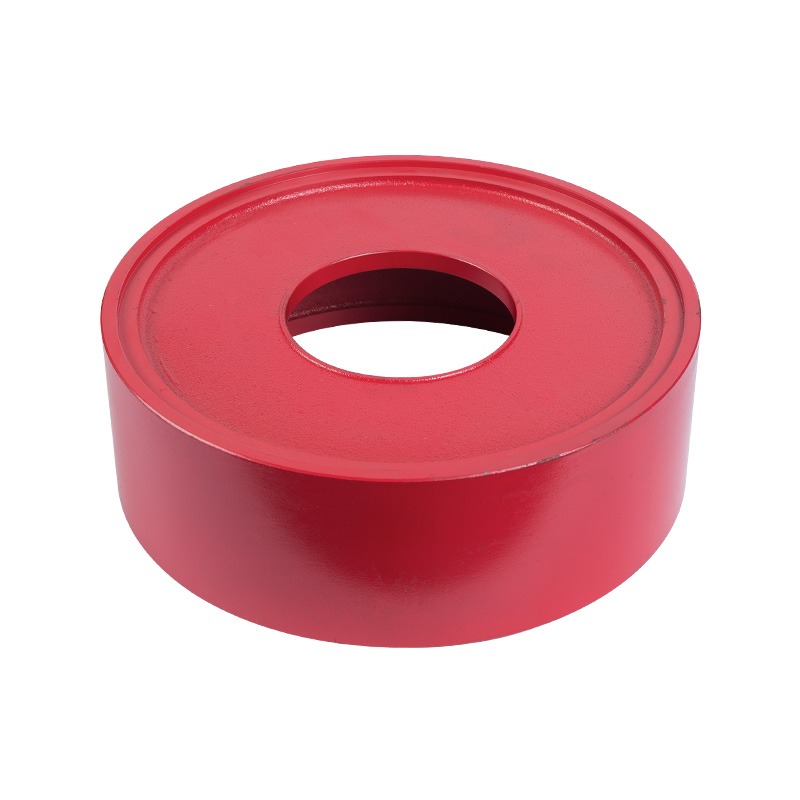

LG multi-stage pump middle section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The middle section is the main part of the pump body, responsible for ...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump motor bracket
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Motor bracket is a support part used to fix the motor and connect the ...
See Details -
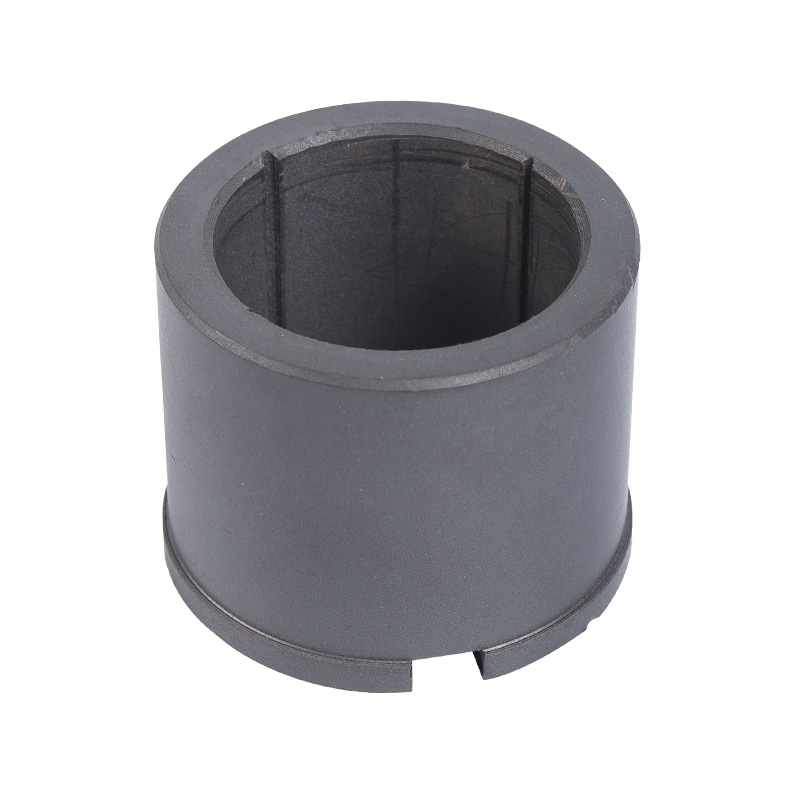

LG multi-stage pump water bearing
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearings are a special type of bearings commonly used in multi-s...
See Details -
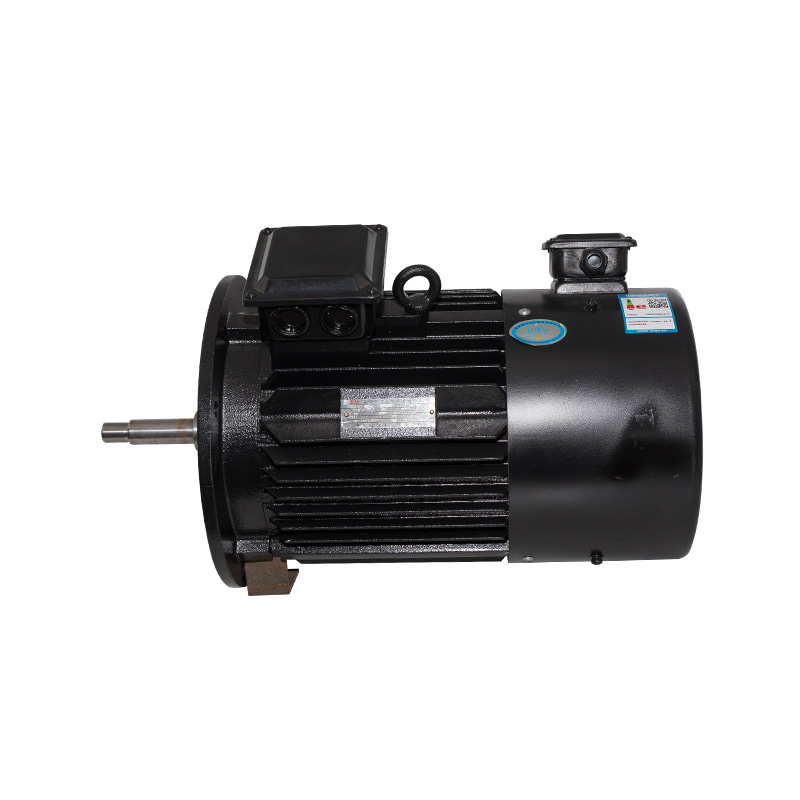

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details -
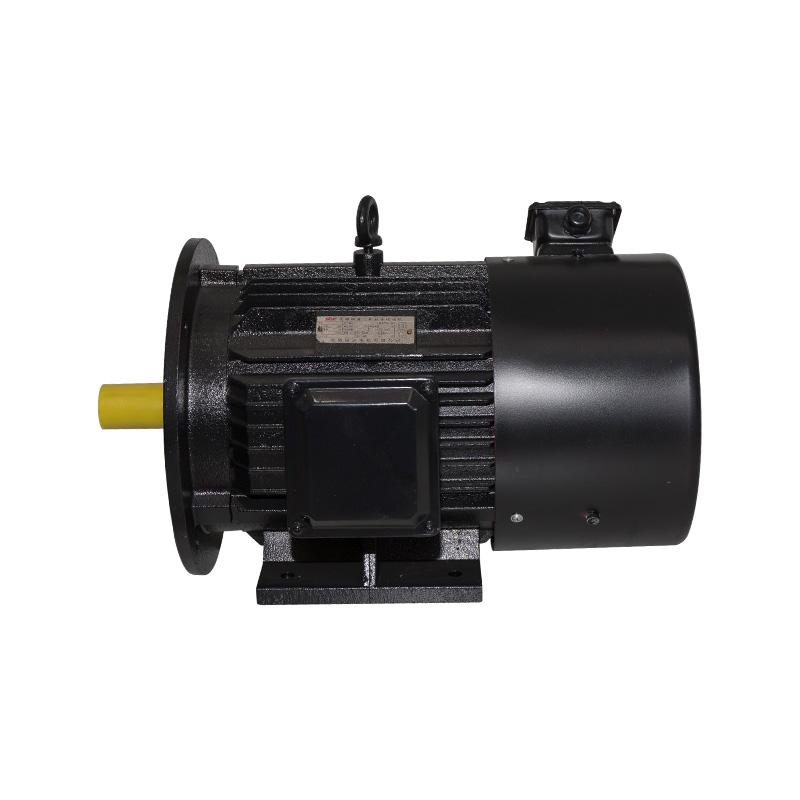

B3/B35 Horizontal inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
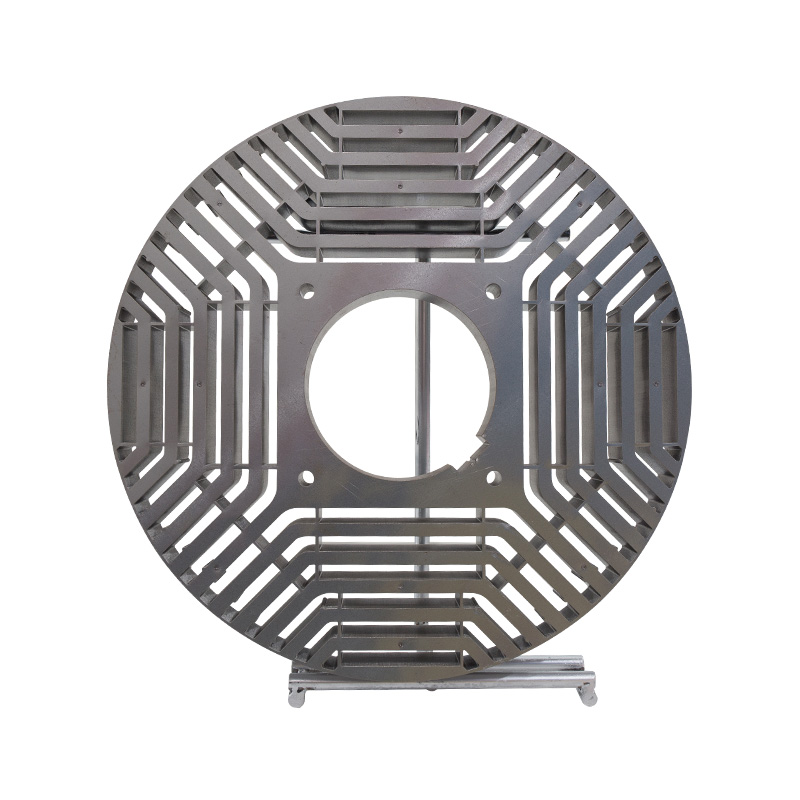

Permanent magnet core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A type of rotor core that uses a permanent magnet material to achieve ...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

