- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Can pipeline pumps handle varying flow rates and pressures, and if so, how do they adjust?
One of the key mechanisms by which pipeline pumps adjust to varying flow rates and pressures is through speed control. By utilizing variable frequency drives (VFDs) or similar speed control mechanisms, pipeline pumps can modulate the rotational speed of their impellers. This speed modulation directly influences the pump's flow rate, allowing it to match the required flow rates within the system.
During periods of high demand, such as peak water usage hours in municipal water supply networks, pipeline pumps can increase their rotational speed to deliver a higher flow rate. Conversely, during times of reduced demand, the pump can operate at a lower speed to match the decreased flow requirements, thus optimizing energy usage and system efficiency.
Pipeline pumps employ pressure control mechanisms to maintain optimal pressure levels within the system. This is crucial for applications where consistent pressure is paramount, such as in HVAC systems, industrial processes, or firefighting systems. Pressure sensors and control systems monitor the pressure at various points in the pipeline. If the pressure exceeds the desired level, the pump can adjust its speed or impeller position to reduce flow and stabilize the pressure. Conversely, if the pressure drops below the target, the pump can increase speed to boost flow and restore the desired pressure.

In scenarios where high-pressure delivery is essential, such as in multi-story buildings or industrial settings, multi-stage pipeline pumps are utilized. These pumps feature multiple impellers arranged in series, with each impeller contributing to increasing the pressure of the fluid as it traverses through the pump stages. The number of stages engaged can be adjusted based on the required pressure, allowing for precise pressure control and efficient operation.
Modern pipeline pump systems often integrate advanced automation and control technologies. These systems continuously monitor flow rates, pressures, and other relevant parameters in real-time. Based on the data collected, the automation systems can autonomously adjust pump speed, impeller position, valve settings, and even switch between multiple pumps as needed. This level of automation not only ensures optimal performance but also enhances energy efficiency by dynamically responding to demand variations.
Related Products
-

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump body
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
Vertical TD Energy Efficient Circulating Pump Pump Body is the shell o...
See Details -

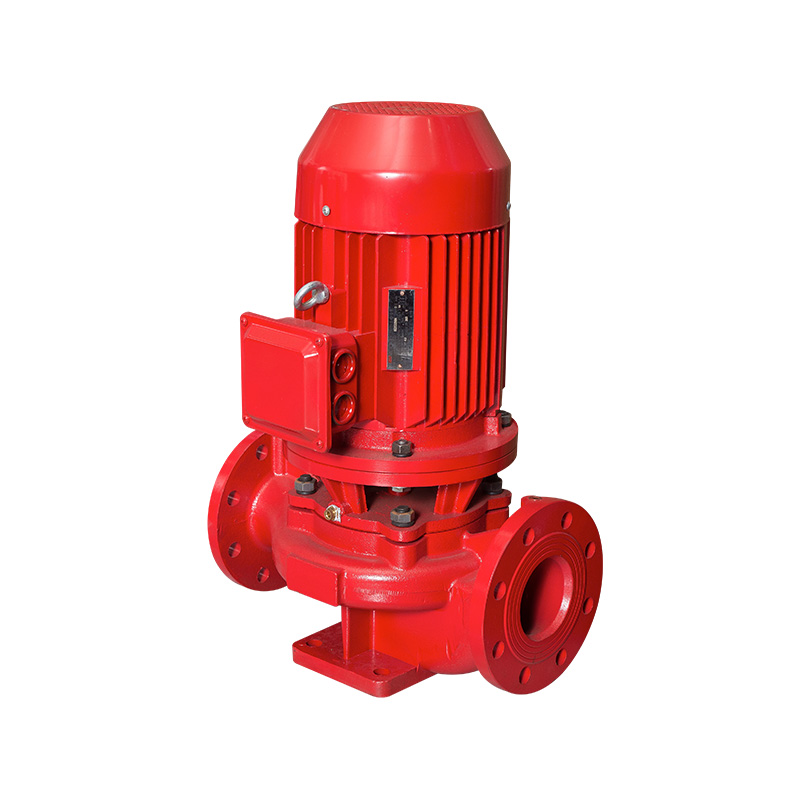
Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
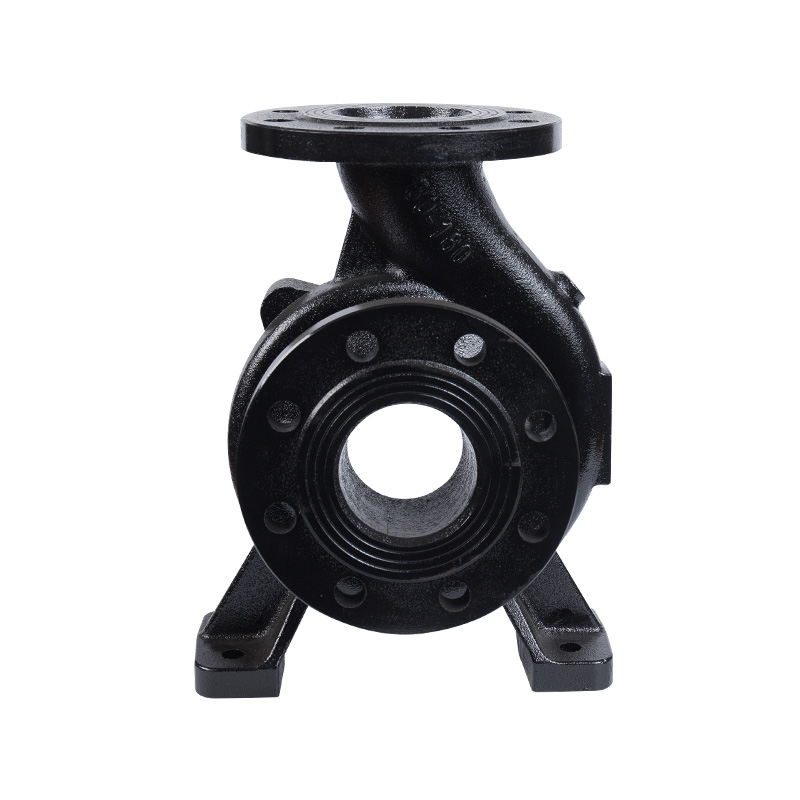

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
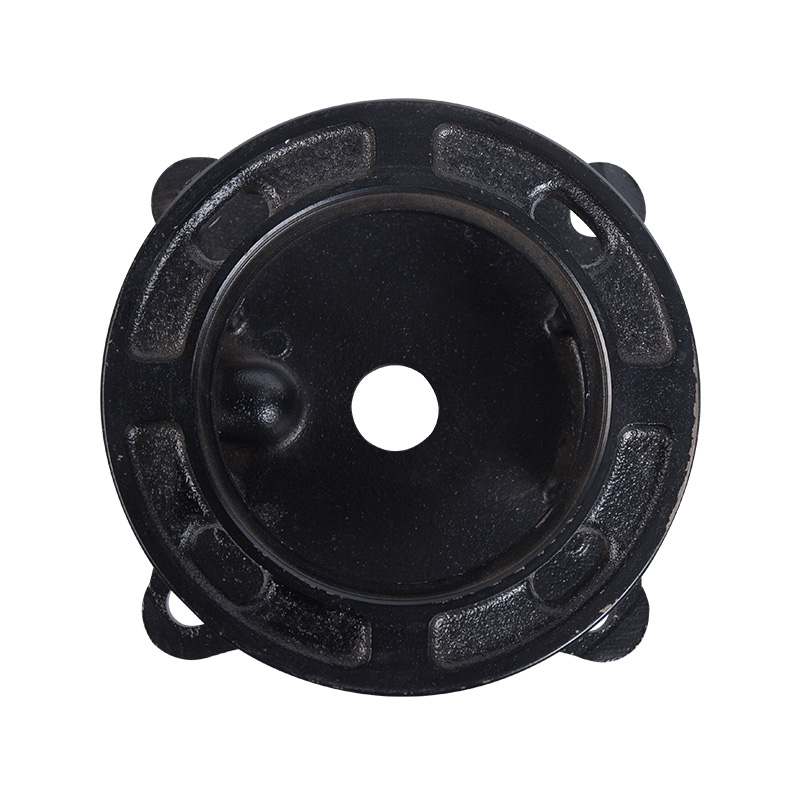

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -
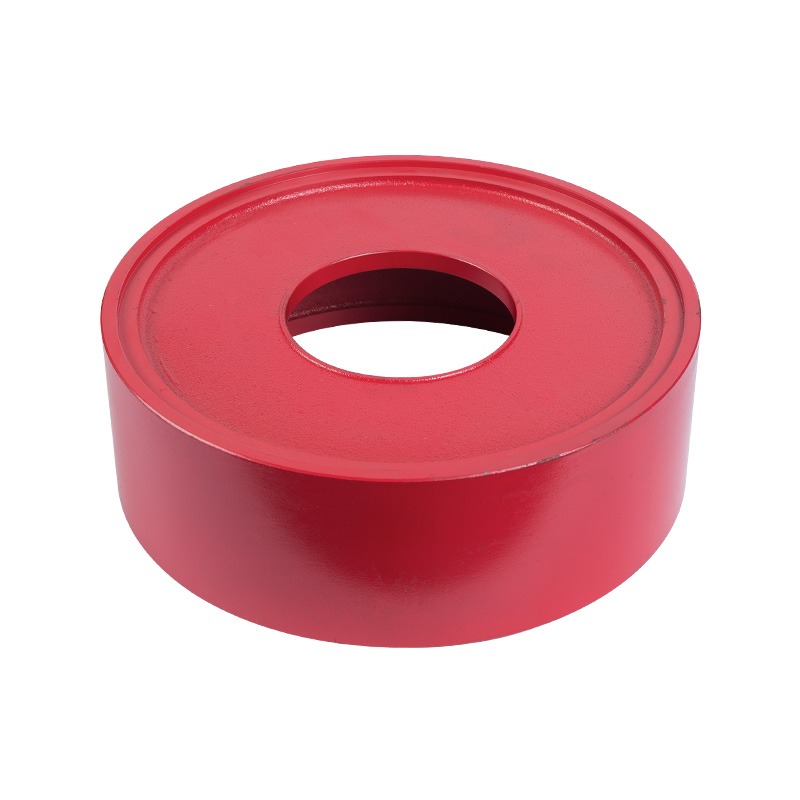

LG multi-stage pump middle section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The middle section is the main part of the pump body, responsible for ...
See Details -
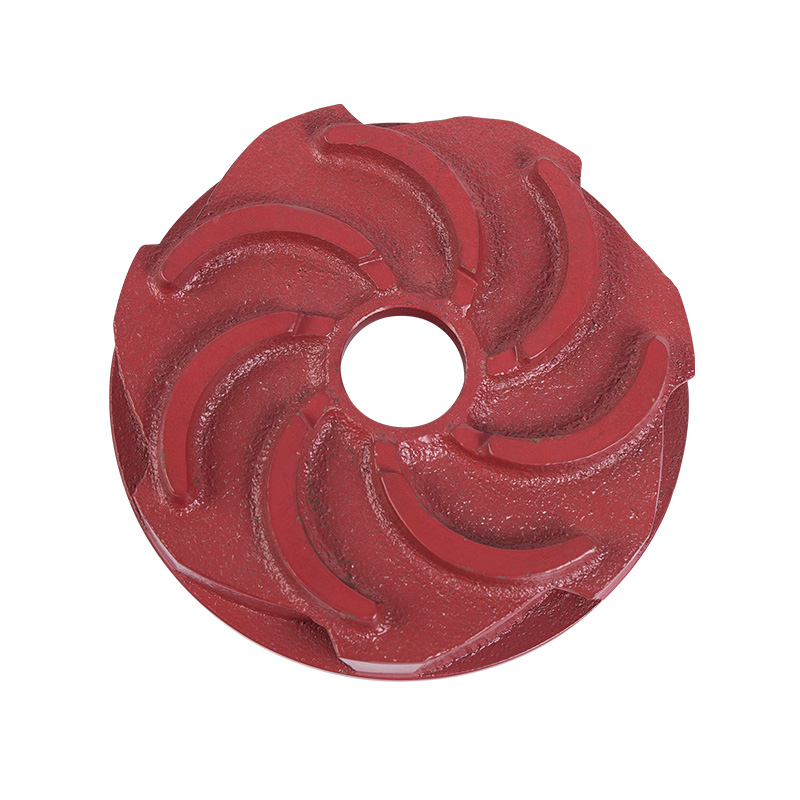

LG multi-stage pump guide vane
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
A guide vane is a guiding device located at the impeller inlet that gu...
See Details -
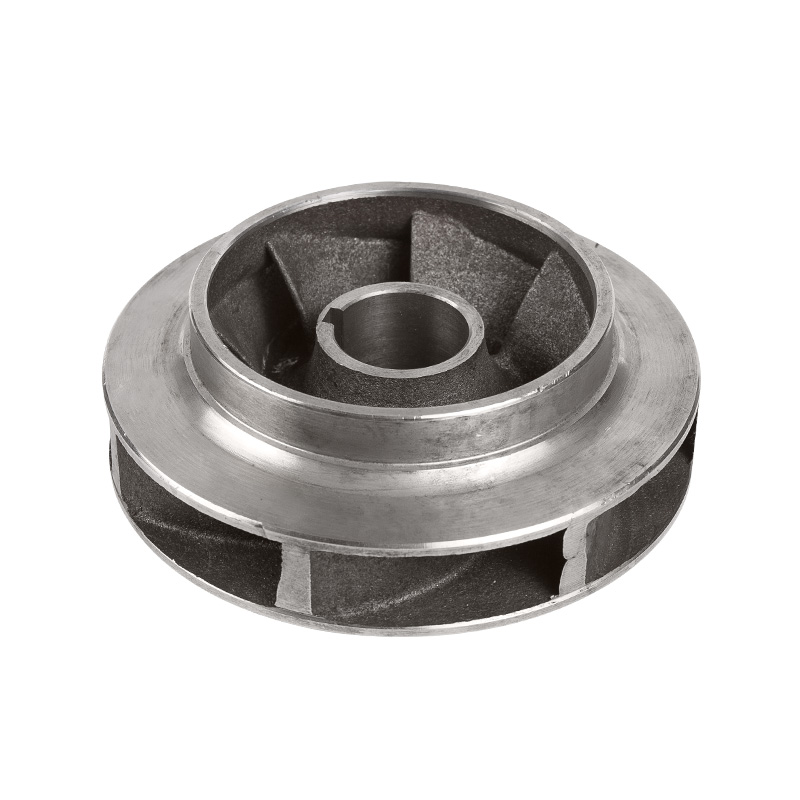

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
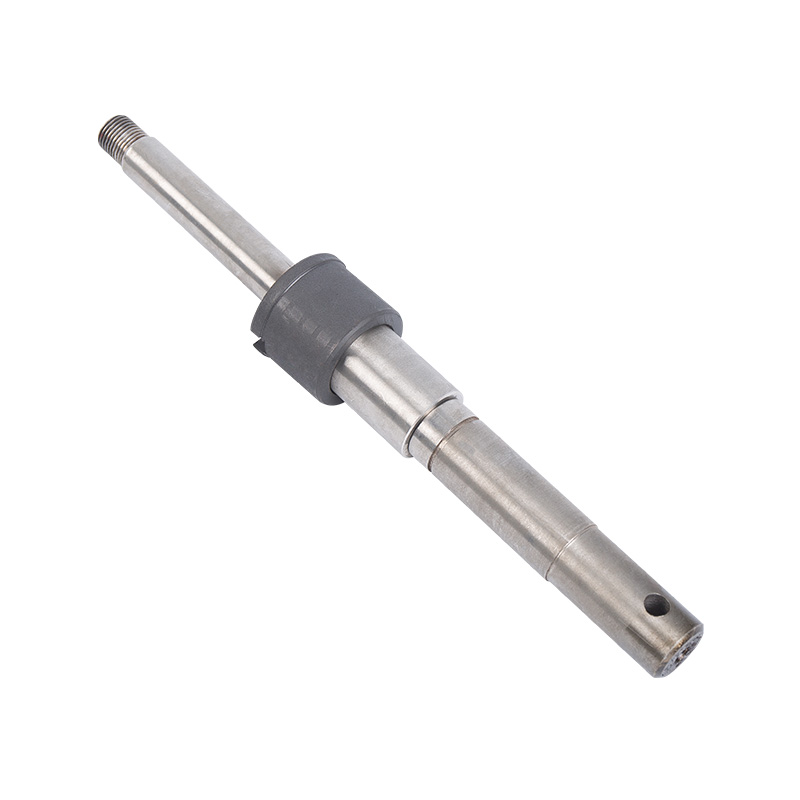

LG multi-stage pump shaft
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the key component to bear the rotational force and t...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump motor bracket
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Motor bracket is a support part used to fix the motor and connect the ...
See Details -
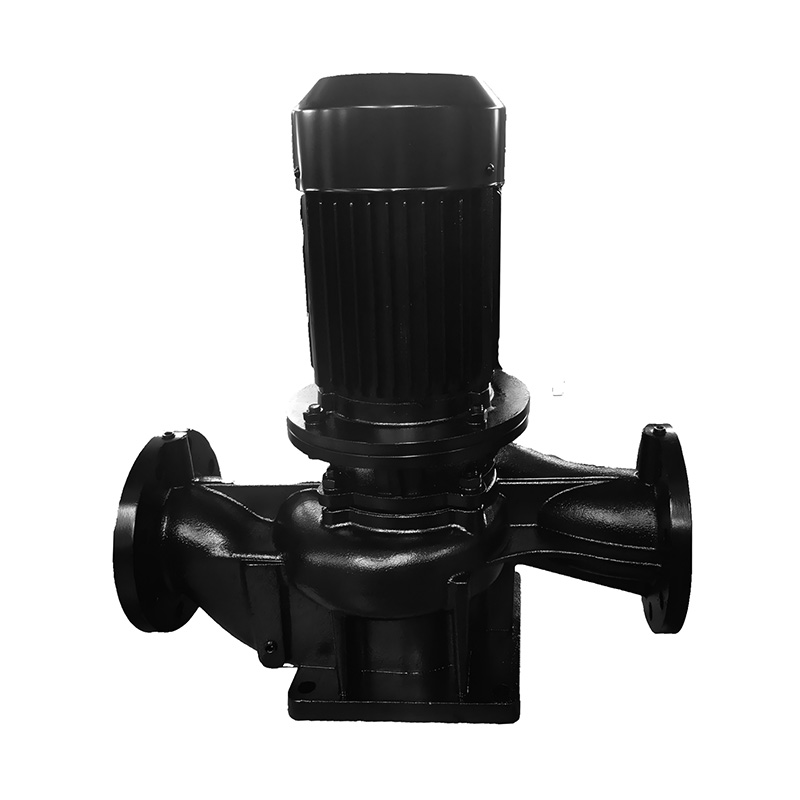

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

