- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
How do the various components of a pipeline pump work together?
After the motor starts, the rotational force is transmitted to the pump shaft through the coupling. The pump shaft is connected to the impeller, driving it to rotate at high speed. The design of the impeller allows it to generate centrifugal force during rotation, which sucks the fluid into the pump body and pushes it towards the outlet.
The pump casing provides a closed space for the rotation of the impeller. Small holes on the pump casing allow water to flow in or out of the impeller, thereby maintaining the normal operation of the pipeline pump. The pump casing also acts as a support and fixation, ensuring the relative stability of all components.
The sealing device plays a crucial role between the pump body and the impeller, preventing liquid leakage from the pump and external air from entering. Components like sealing rings ensure effective closure of the gap between the pump casing and the pump shaft, further enhancing the sealing effect.
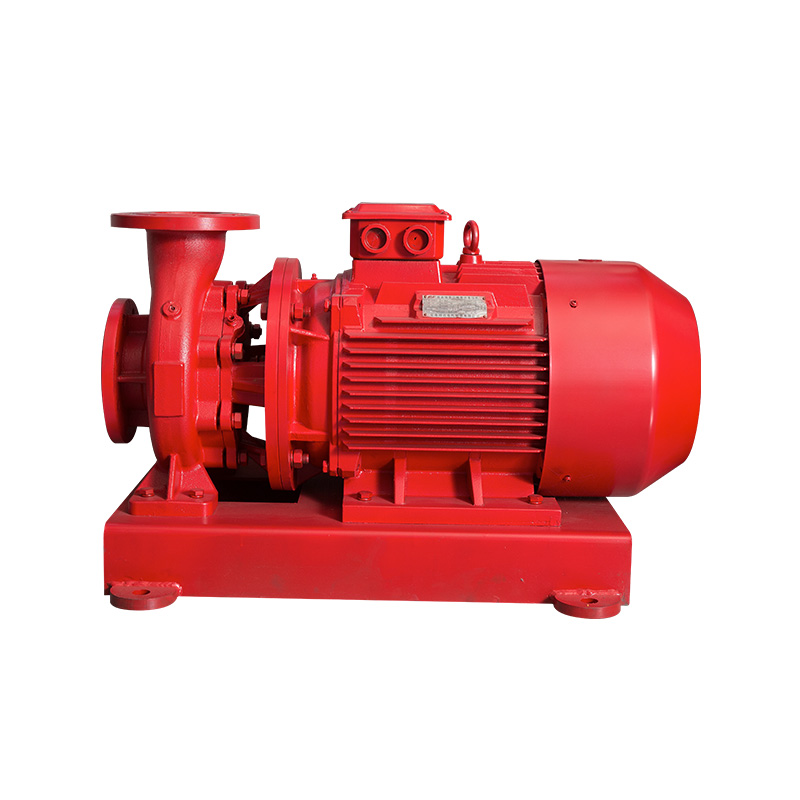

Bearings are responsible for supporting the pump shaft, reducing friction and wear during its rotation. A good bearing condition is essential for maintaining the smooth rotation of the pump shaft, thus ensuring the stable operation of the impeller.
During the operation of the pipeline pump, attention must also be paid to the flow of the liquid. When the liquid is pushed to the outlet by the impeller, the control valve regulates the outlet pressure and flow rate. Additionally, the outlet valve of the pipeline pump can further regulate the fluid flow to ensure a stable and continuous flow in the pipeline.
The various components of the pipeline pump work together to achieve functions such as suction, pushing, and flow control of the liquid. Their coordination ensures the efficient and stable operation of the pipeline pump, providing reliable power support for liquid transportation.
Related Products
-

Pipe pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump cover is used to tighten and seal. The pump cover ensures tha...
See Details -

Sewage pump body
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The pump body is the outer shell of the sewage pump, with the function...
See Details -

Sewage pump cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the top of the sewage pump unit, it is used to enclose th...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump shaft
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the key component to bear the rotational force and t...
See Details -

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details -

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details -

Motor core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A common motor structure, the stator is fixed by the iron core structu...
See Details -

Permanent magnet core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A type of rotor core that uses a permanent magnet material to achieve ...
See Details -

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

