- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
How does a circulating pump work through a closed loop system?
Principle of Operation: Circulator pumps operate based on the principle of centrifugal force. They use an impeller, which is a rotating component with curved blades, to create centrifugal force that pushes the fluid outward from the center of the impeller.
Inlet and Outlet Ports: A circulator pump typically has two ports: an inlet port and an outlet port. The pump is installed in the fluid circulation loop with the inlet connected to the supply side of the system and the outlet connected to the return side.
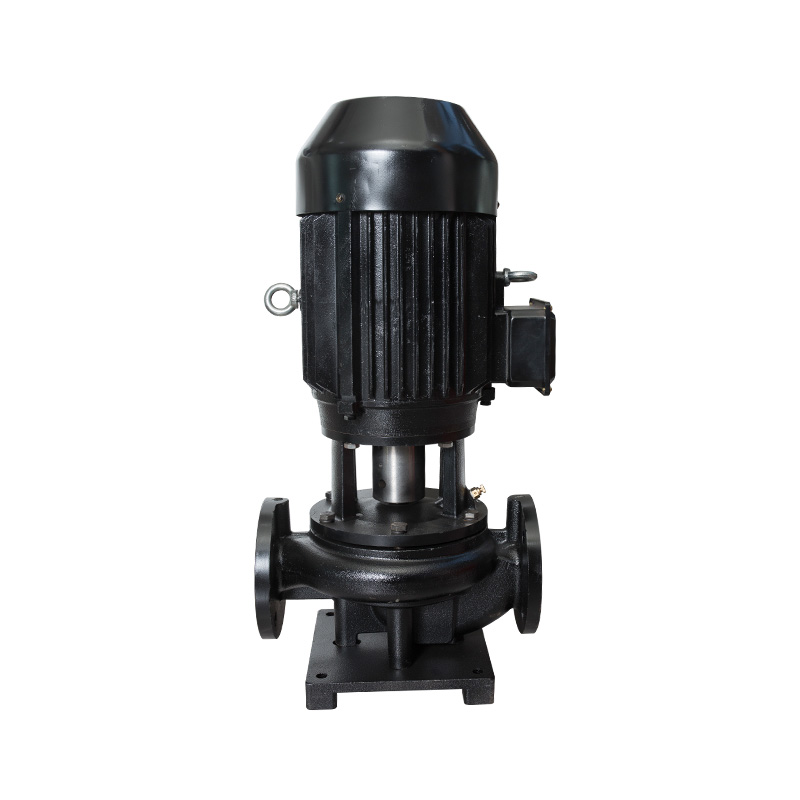

Impeller Rotation: When the pump is powered on, the impeller rotates rapidly within the pump housing. As the impeller spins, it creates a low-pressure zone at the center and a high-pressure zone at the outer edges due to centrifugal force.
Fluid Intake: Fluid from the supply side of the system enters the pump through the inlet port. The low-pressure zone created by the rotating impeller draws the fluid into the pump.
Centrifugal Force: As the fluid enters the pump, it is directed towards the center of the impeller and then forced outward towards the outer edges of the impeller blades by centrifugal force. This action increases the fluid pressure and velocity.
Fluid Discharge: The pressurized fluid is then discharged from the pump through the outlet port. It travels through the circulation loop, delivering heat or hot water to the desired areas of the system.
Continuous Circulation: Circulator pumps maintain continuous circulation of the fluid within the closed-loop system, ensuring efficient heat distribution or hot water delivery. The pump operates continuously or intermittently based on the system's heating or water demand.
Control and Regulation: Circulator pumps may be equipped with controls or variable-speed settings to regulate the flow rate and optimize energy efficiency. Advanced circulator pumps may also have sensors or feedback mechanisms to adjust pump speed or operation based on system conditions or user preferences.
Circulator pumps play a vital role in maintaining the flow of water or other fluids within closed-loop systems, ensuring efficient heat transfer in hydronic heating systems and providing instant hot water delivery in hot water recirculation systems. Their simple yet effective design allows for reliable and continuous operation, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
Related Products
-

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
The TD type single-stage pipeline circulation pump is a green, environ...
See Details -

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -

LG multistage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Cast iron impeller is one of the key components of the pump, which pre...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -

Stainless steel LG multi-stage pump bearing sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless Steel Bearing Sleeves are bearing sleeves made of stainless ...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump spacer sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Spacer sleeve is a ring-shaped part installed between the impellers of...
See Details -

Vertical motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
A conventional fixed-speed motor whose operating speed is usually cons...
See Details -

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details -

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

