- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Electric Motors: The Heart of Modern Technology
Electric motors are integral components in almost every device we use today, from household appliances and industrial machinery to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Their efficiency, versatility, and reliability make them the backbone of modern technology, driving innovation in various sectors.
Electric motors can be classified into two primary categories based on the type of current they use: AC motors and DC motors.
These motors are powered by alternating current, where the direction of the current periodically changes. AC motors are the most common type used in both domestic and industrial applications due to their simple construction, durability, and efficiency. They can be further divided into:
Also known as asynchronous motors, these are the most widely used in industries. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the current is induced in the rotor by the magnetic field generated by the stator. Induction motors are reliable, cost-effective, and used in applications like fans, pumps, and conveyor belts.
These motors run at a constant speed, synchronized with the frequency of the AC supply. Synchronous motors are used in applications where precise speed control is required, such as in power generation plants and large-scale machinery.
Powered by direct current, DC motors offer precise speed control and high starting torque. They are used in applications where variable speed and smooth control are necessary, such as in electric vehicles, robotics, and portable tools. DC motors can be further divided into:

These motors use a mechanical commutator and brushes to reverse the current direction in the windings. They are simple, inexpensive, and commonly used in small devices like toys and appliances.
These motors do not use brushes, reducing wear and improving efficiency and longevity. BLDC motors are often found in high-performance applications, such as drones, computer hard drives, and electric vehicles.
Electric motors are found everywhere, powering a vast array of devices and systems. Here are some key applications:
Many household items, such as refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, and air conditioners, rely on electric motors. These motors provide the necessary mechanical movement for various tasks, like turning fans, pumps, and compressors.
Electric motors are at the heart of electric vehicles, providing propulsion and driving the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors in EVs offer instant torque and high efficiency, contributing to the growing popularity of electric transportation and the shift towards greener alternatives.
In industries, electric motors power conveyor belts, cranes, pumps, and fans, among other machinery. These motors enable automated processes, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing production efficiency.
Electric motors play a critical role in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar power systems. Wind turbines, for example, use electric motors to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Similarly, motors are used in solar water pumps and other renewable energy applications, supporting the transition to sustainable energy sources.
Robots depend heavily on electric motors for movement and precision. DC motors, in particular, are used in robotic arms, drones, and autonomous vehicles, offering precise control over speed, direction, and torque.
The demand for electric motors is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for energy-efficient solutions. Some key trends shaping the future of electric motors include:
As energy consumption becomes a growing concern, manufacturers are developing motors that are more efficient and sustainable. Innovations like permanent magnet motors, which use high-efficiency magnets, and developments in motor cooling technologies are helping to improve performance while reducing energy consumption.
The integration of electric motors with the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart technologies will allow for real-time monitoring and control. Smart motors that can communicate with other devices will enable predictive maintenance, remote operation, and energy optimization.
Electric motors are increasingly being used in the transportation sector, not only in cars but also in aircraft and ships. Electric aircraft powered by motors will reduce emissions and lower operating costs, while electric ships will offer a greener alternative to traditional marine propulsion systems.
Advances in materials and manufacturing techniques will lead to more compact and lightweight electric motors. Smaller, high-power motors will enable the development of next-generation portable devices, wearables, and even medical implants.
Related Products
-

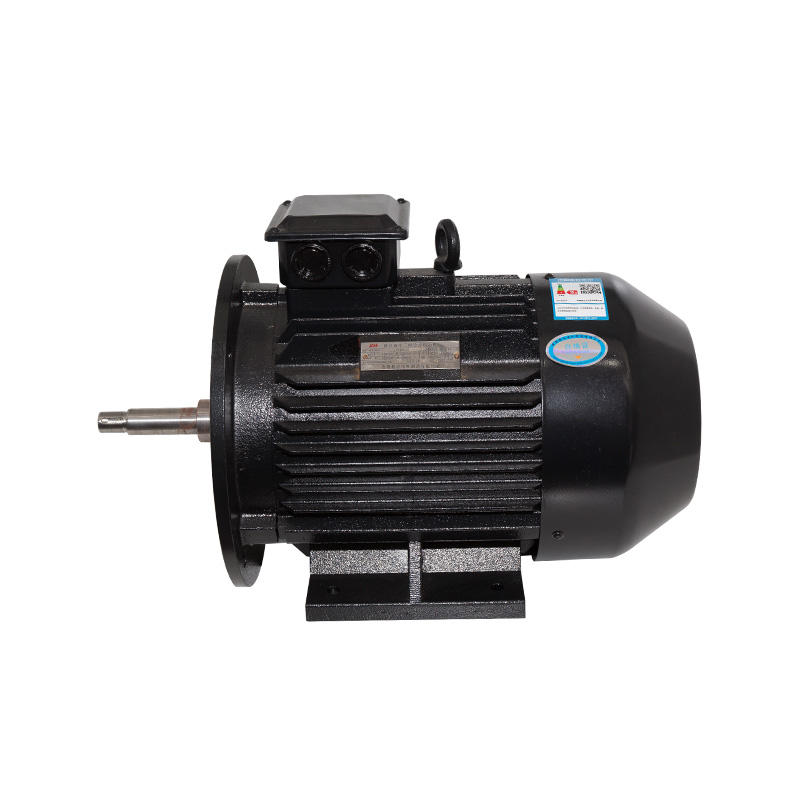
Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
The TD type single-stage pipeline circulation pump is a green, environ...
See Details -

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump body
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
Vertical TD Energy Efficient Circulating Pump Pump Body is the shell o...
See Details -
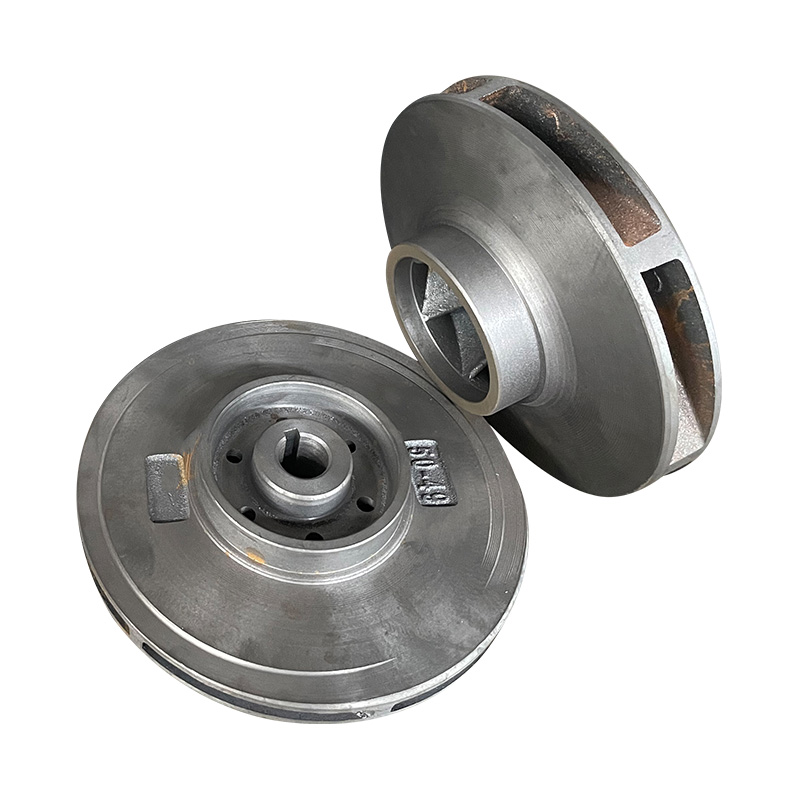

TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulating pump cast iron impeller
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
TD Energy Efficient Circulation Pump Cast Iron Impeller is an importan...
See Details -

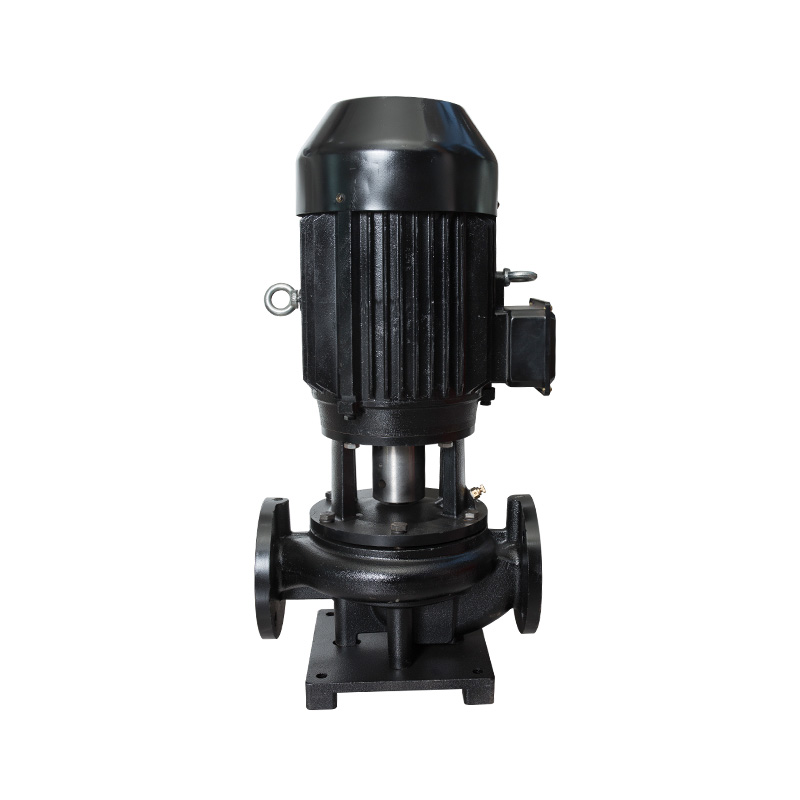
Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
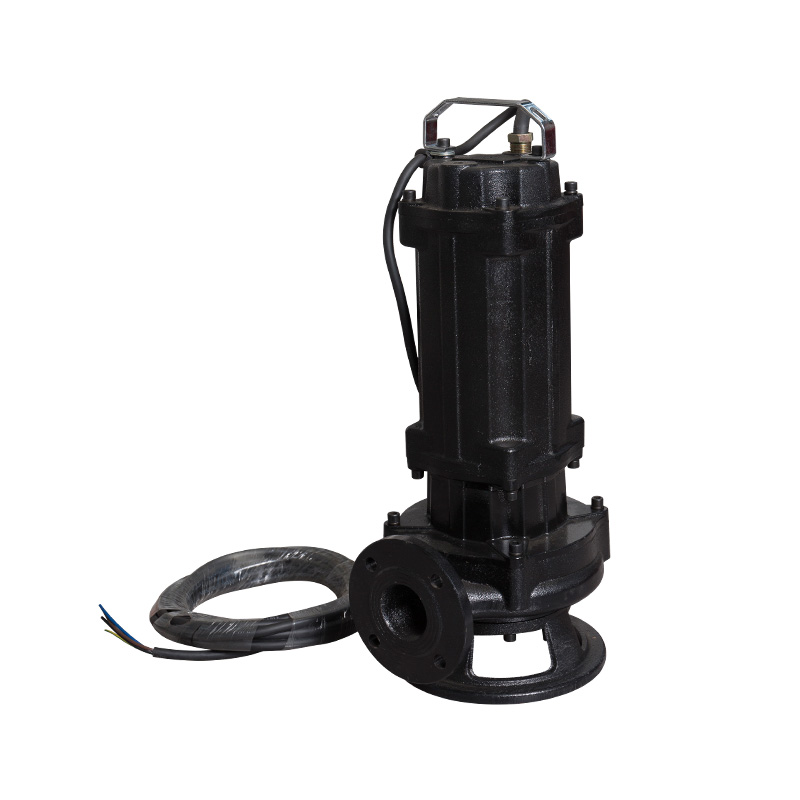

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
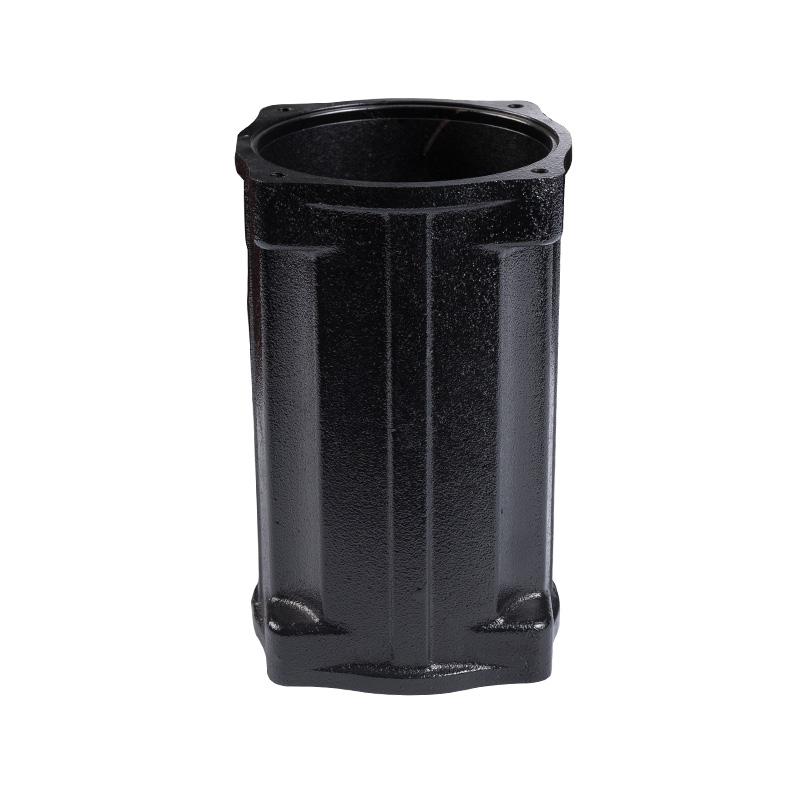

Sewage pump casing
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The casing of the sewage pump unit plays a role in protecting the inte...
See Details -
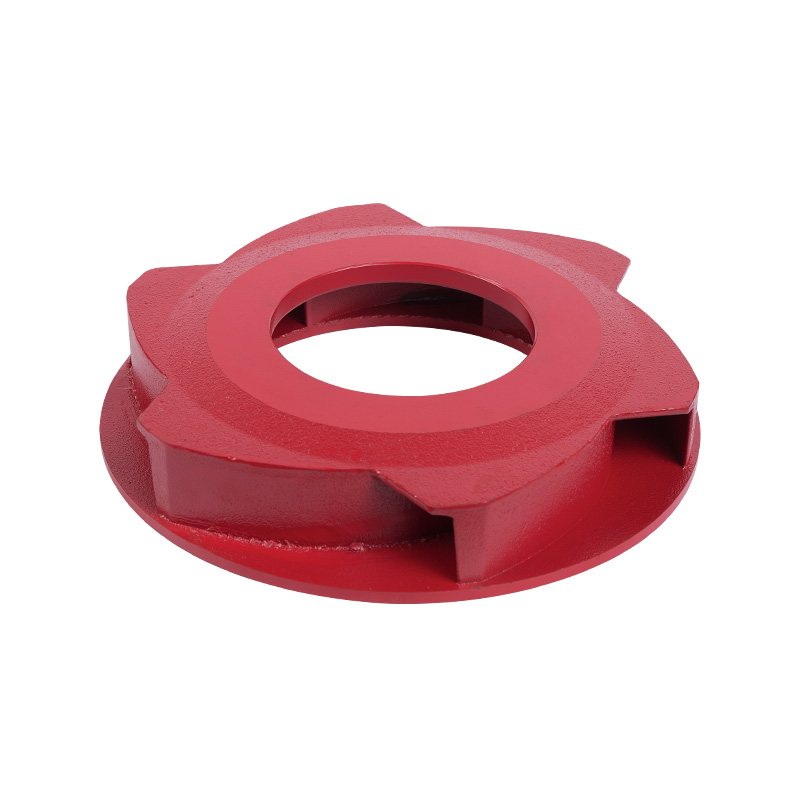

LG multistage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Cast iron impeller is one of the key components of the pump, which pre...
See Details -
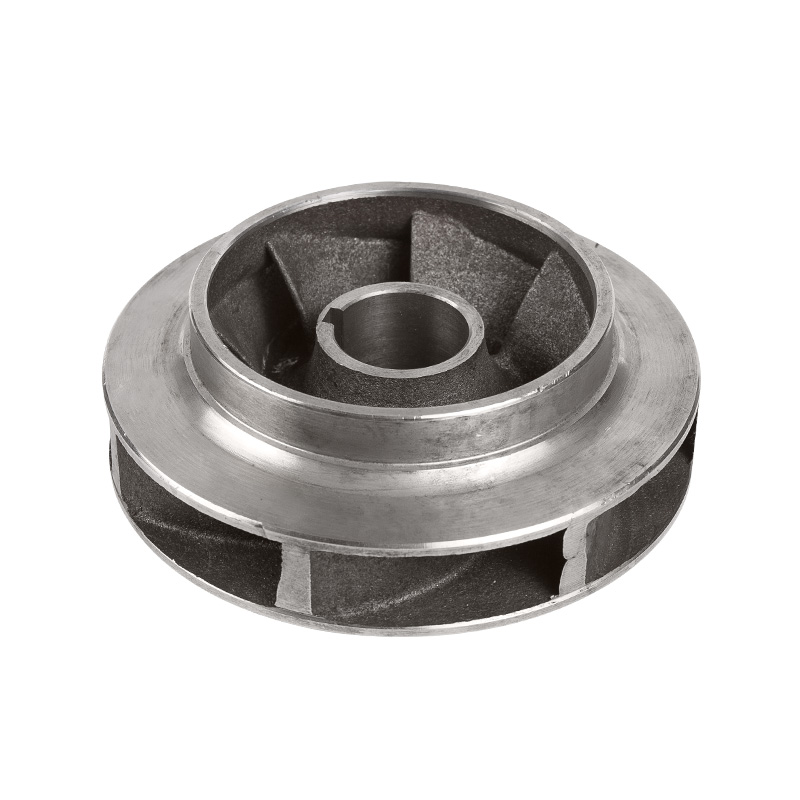

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
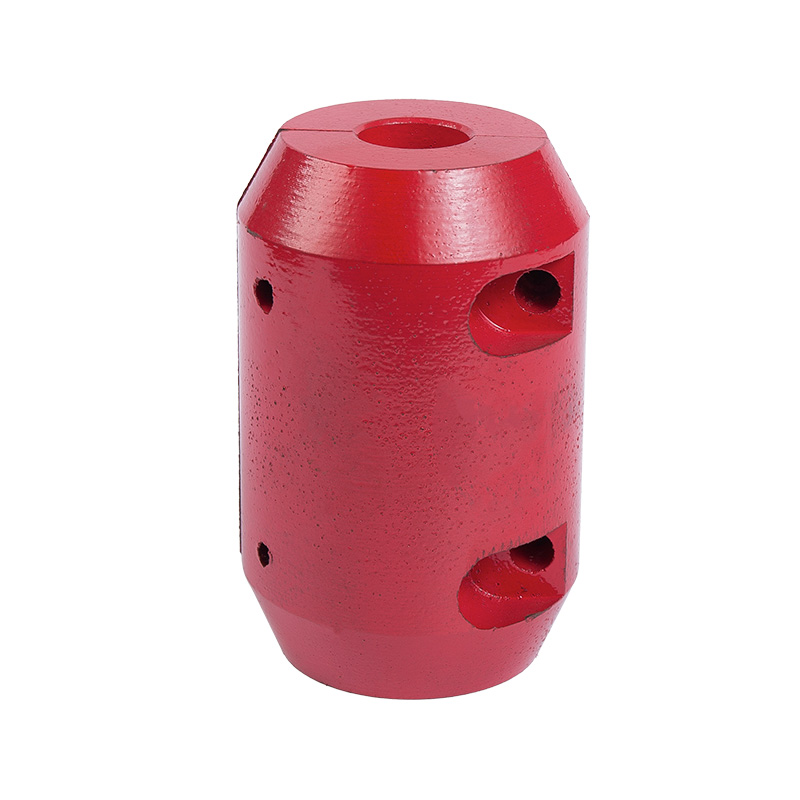

LG multi-stage pump coupling
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Couplings are used to connect the pump shaft to the motor shaft for en...
See Details -
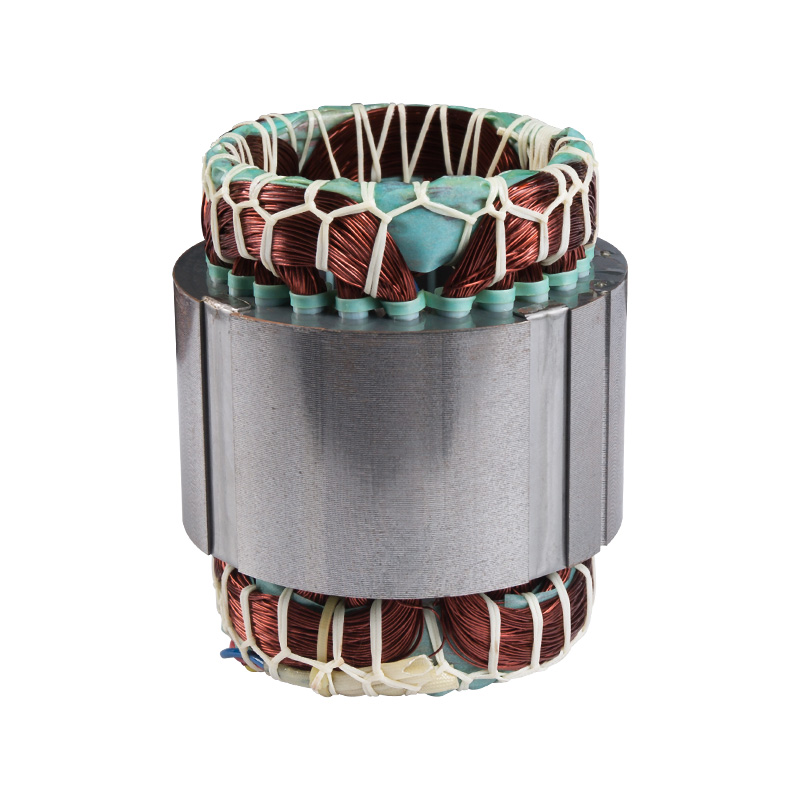

Finished stator
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The stator of a motor refers to the fixed part which contains the stat...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

