- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Electric Motors: The Backbone of Modern Technology and Innovation
Electric motors are among the most crucial inventions in the history of technology, playing a pivotal role in nearly every sector of modern life. From the everyday appliances we use to large industrial machines, electric motors drive innovation, efficiency, and productivity. These versatile machines convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering everything from household fans to electric cars.
The fundamental principle behind electric motors is the electromagnetic effect, discovered by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820. Ørsted found that an electric current creates a magnetic field, which in turn can be used to generate motion. This discovery laid the groundwork for the development of electric motors.
Electric motors can be classified into several types, each suited for different applications depending on their design, operation, and the power source they use. The two primary categories of electric motors are AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) motors. Here's a closer look at each type:
AC Motors AC motors are powered by alternating current, which reverses direction periodically. These motors are widely used in household appliances, industrial machinery, and large-scale power systems. AC motors can be further divided into two main types:
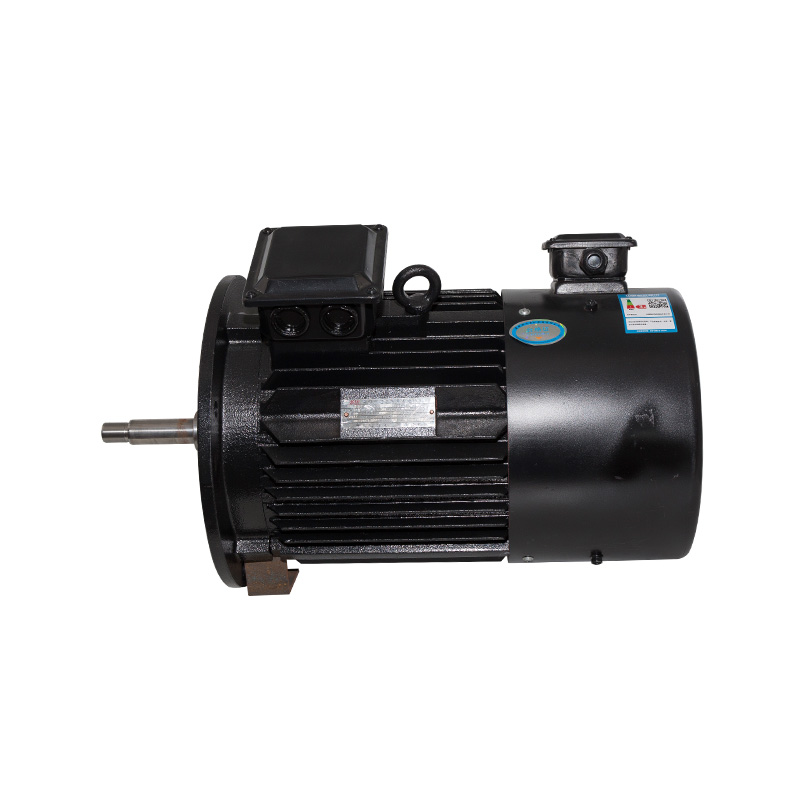

The most commonly used type of AC motor, induction motors are highly efficient and require little maintenance. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the current in the stator (stationary part of the motor) induces a magnetic field in the rotor (the rotating part). This magnetic interaction causes the rotor to turn. Induction motors are used in everything from HVAC systems to washing machines.
These motors operate at a constant speed, synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. They are typically used in high-precision applications such as clocks, large generators, and in systems requiring constant speed.
DC Motors DC motors are powered by direct current, where the flow of electricity remains constant. These motors provide high torque at low speeds and are easier to control than AC motors. DC motors are typically used in applications where speed and direction need to be precisely controlled. DC motors come in several variations:
These motors have a simple design with brushes that transfer current to the motor’s rotor. They are widely used in small devices like power tools, toys, and automotive applications.
In contrast to brushed motors, BLDC motors eliminate the need for brushes, offering higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and smoother operation. They are used in electric vehicles, drones, computer hard drives, and other precision equipment.
Universal Motors Universal motors can operate on both AC and DC power. They are commonly found in small household appliances, such as vacuum cleaners, blenders, and power tools. These motors are versatile and offer high speed and torque but are not as efficient as other motor types.
Stepper Motors Stepper motors are a special type of DC motor that moves in discrete steps, making them ideal for applications requiring precise positioning and control. They are used in devices like printers, CNC machines, and robotics, where exact movement is critical.
At the heart of all electric motors is the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current. Here's a simplified breakdown of the basic working principle of an electric motor:
When electrical power is supplied to the motor, current flows through the motor’s coil (called the armature).
The current flowing through the coil generates a magnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnets (or electromagnets) in the motor. This interaction creates a force that pushes the armature.
The force generated causes the armature to rotate. This rotational motion is transferred to a shaft connected to the motor, which then drives the connected device or machinery.
In DC motors, a commutator (a mechanical switch) is used to reverse the direction of current flow through the coil as it rotates. This keeps the motor turning continuously. In AC motors, the alternating current naturally reverses direction, causing the motor to keep spinning.
The efficiency, torque, and speed of an electric motor depend on various factors, such as the type of motor, the strength of the magnetic field, the current supplied, and the design of the motor components.
Electric motors have revolutionized various industries and become integral to modern life. Some of the most common applications include:
Electric motors are used in a wide range of everyday household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, vacuum cleaners, and kitchen gadgets. These motors provide the mechanical motion needed to perform tasks efficiently.
Electric motors are at the heart of electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid cars, and electric bikes. As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, electric motors are becoming more prominent in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact.
Electric motors power large machines in factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants. They drive conveyor belts, pumps, fans, compressors, and other essential equipment that keep production lines running smoothly.
The development of robotics heavily relies on electric motors, particularly stepper motors and brushless DC motors, to achieve precise movement and control. Electric motors also power automated systems in industries like logistics, agriculture, and healthcare.
Electric motors are used in wind turbines, hydroelectric generators, and other renewable energy technologies to convert mechanical energy into electricity. These systems are helping to reduce global dependence on fossil fuels and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Electric motors are critical components in medical devices, including ventilators, infusion pumps, diagnostic machines, and prosthetics. They provide the power needed for these life-saving devices to function efficiently.
Electric motors are continuously evolving, with advancements focused on improving efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing performance. Innovations such as magnetless motors, smart motors, and nanomaterials hold the potential to revolutionize the industry even further. With the growing focus on clean energy and automation, electric motors will continue to be at the forefront of technological progress in both consumer products and industrial applications.
Related Products
-
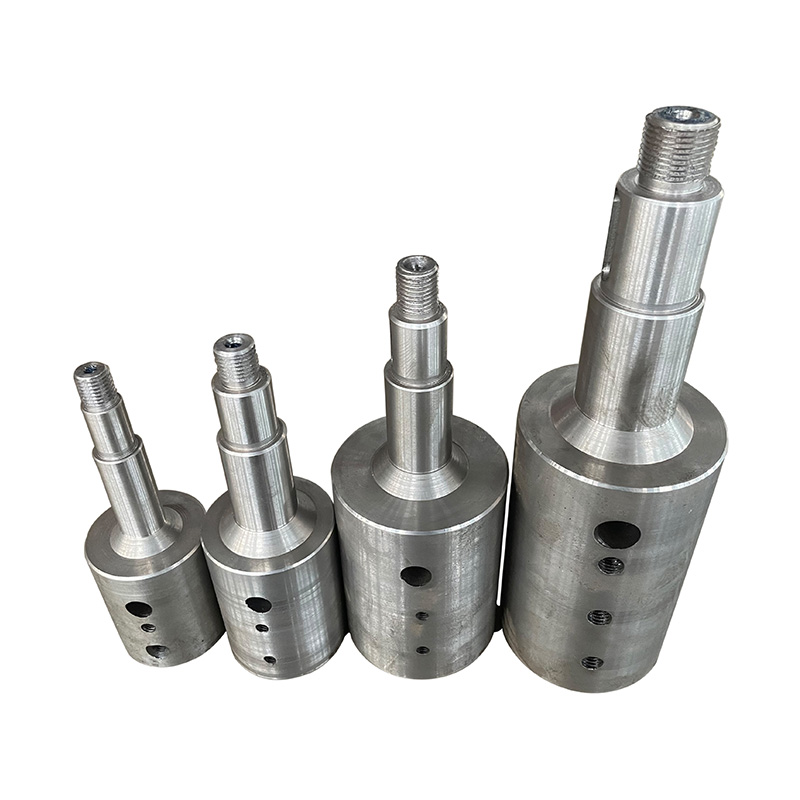

TD high efficiency and energy saving circulating pump pump shaft
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the component that connects the motor to the impelle...
See Details -

Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
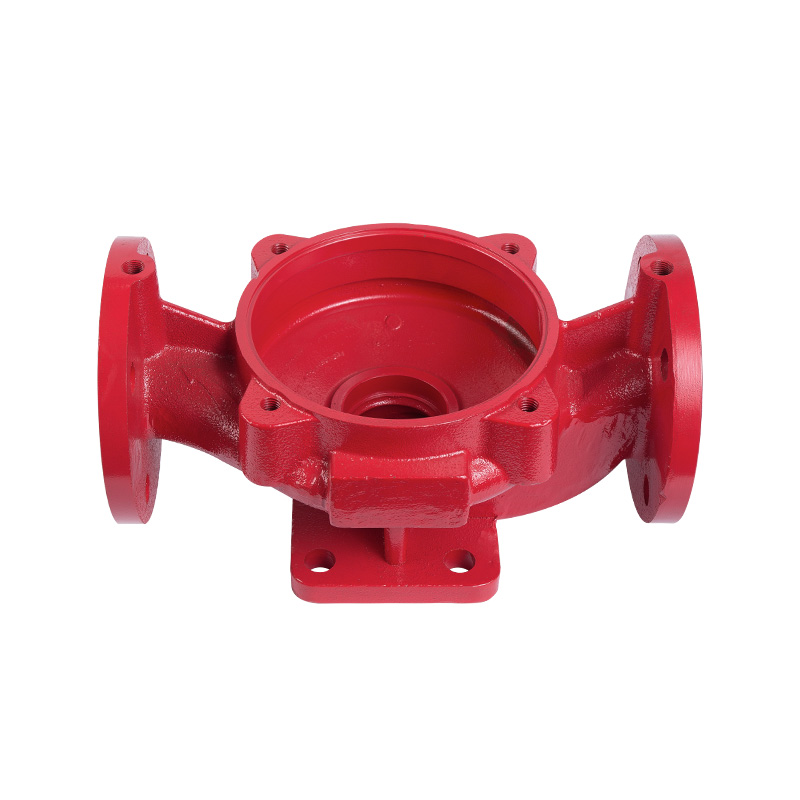

Vertical pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
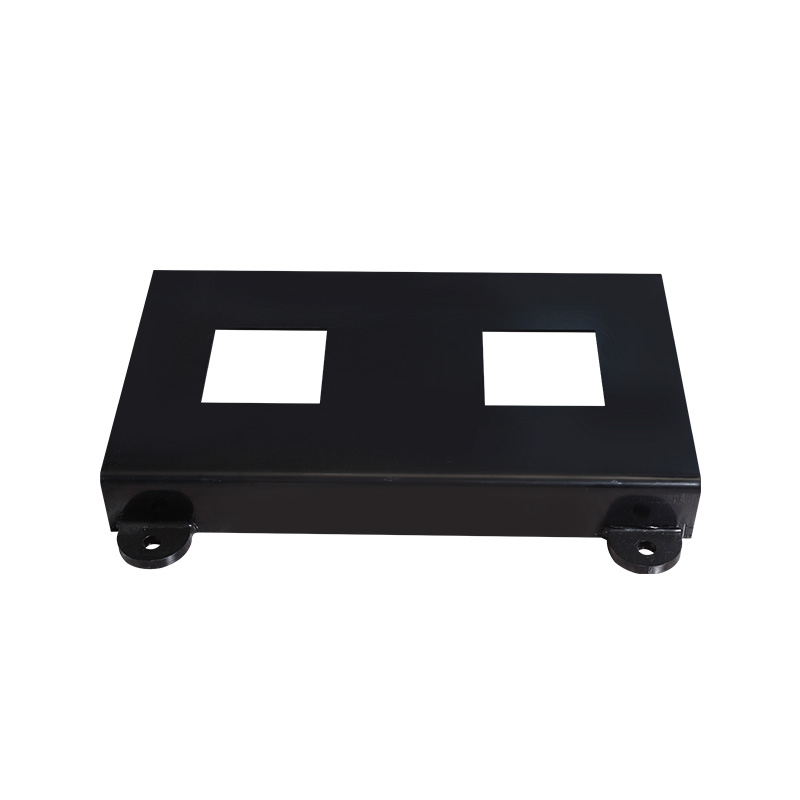

Pipe pump horizontal base
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump base serves to support and secure the pump casing. Horizontal...
See Details -
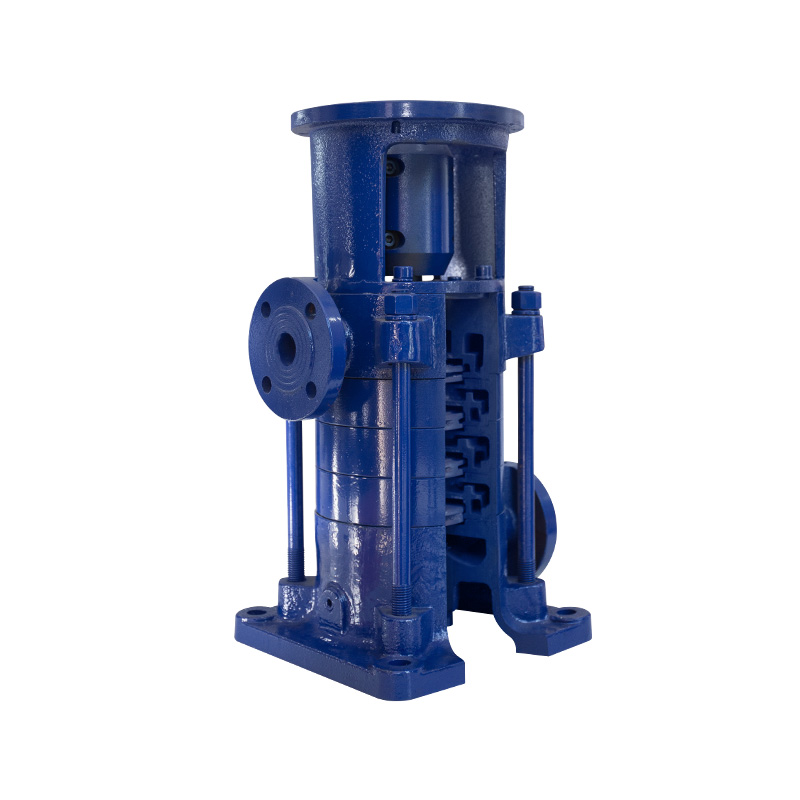

LG multistage pump 100 series
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump
Product features 1. Compact structure, small volume, small footprint. ...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump motor bracket
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Motor bracket is a support part used to fix the motor and connect the ...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump water bearing gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearing gland is the gland for fixing the water bearing, which s...
See Details -
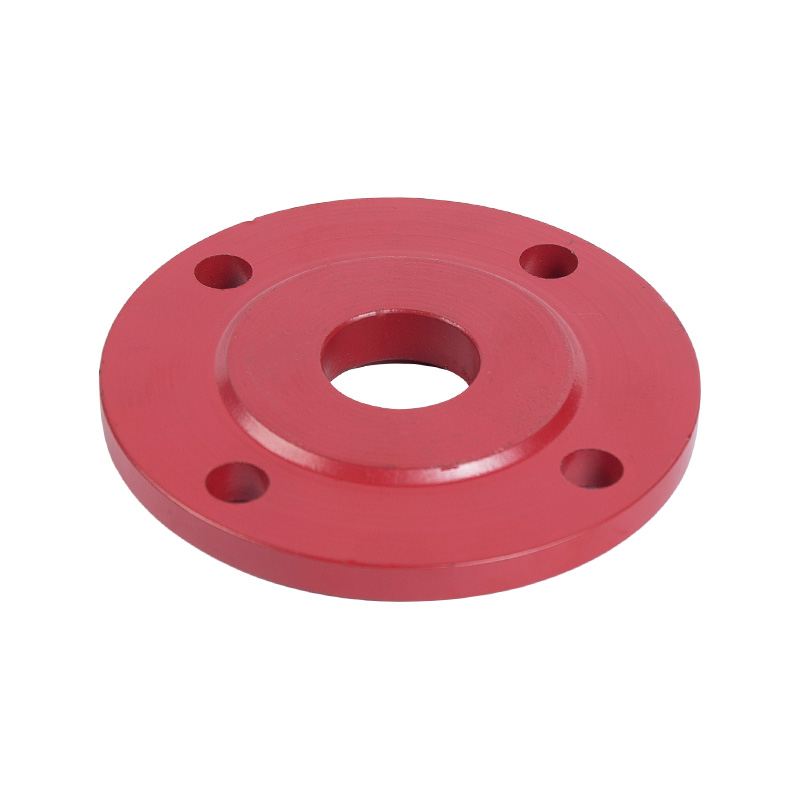

LG multi-stage pump seal gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The machine seal gland is a component that encloses the machine seal u...
See Details -
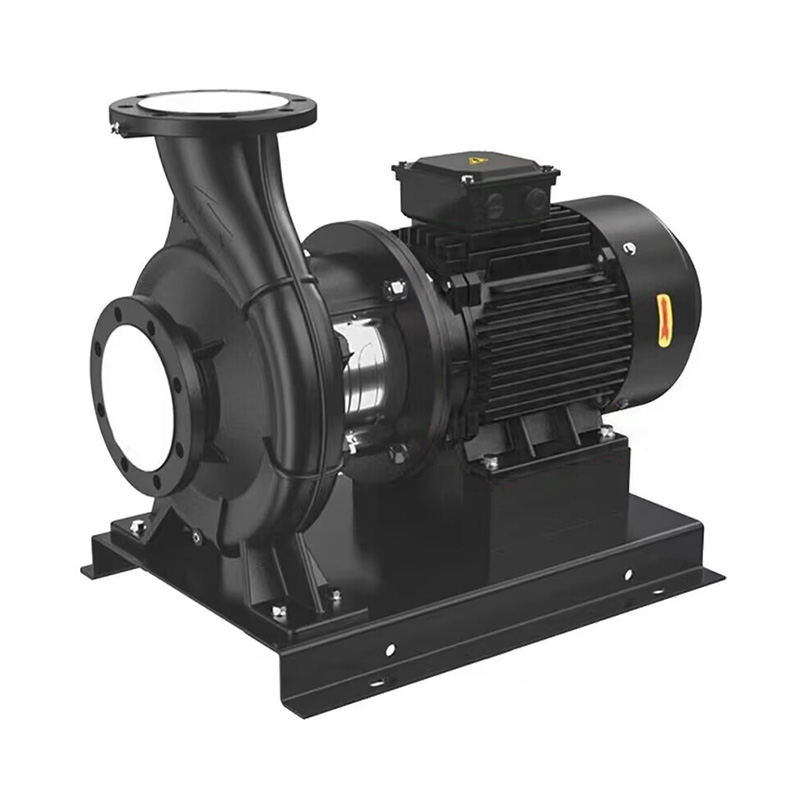

TD horizontal high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
1.TD horizontal high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump is ...
See Details -
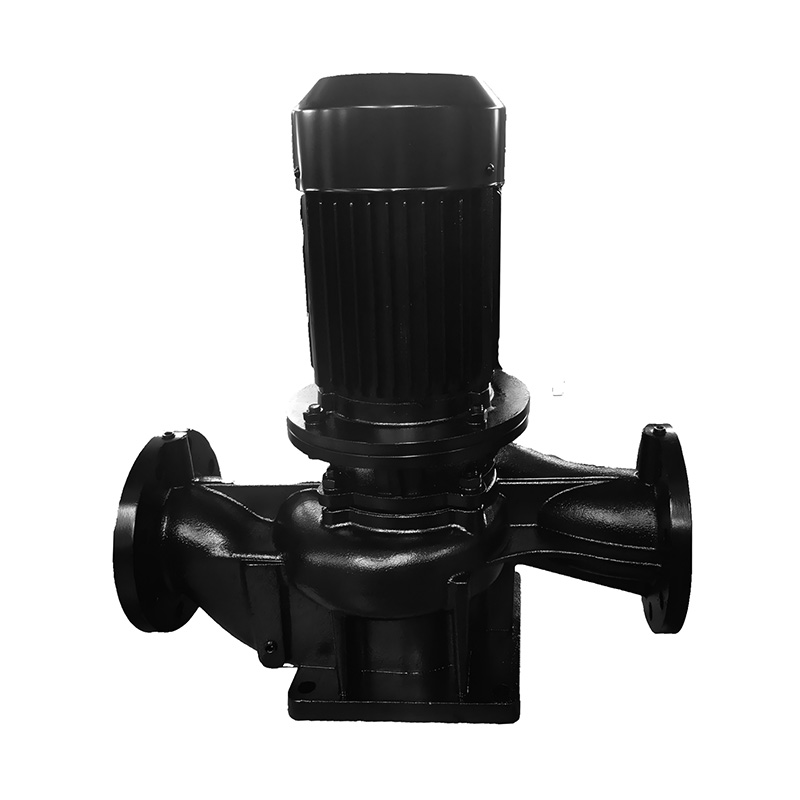

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

