- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Role Does the Electric Motor Stator Play in Enhancing Motor Efficiency and Performance?
The electric motor stator is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the operation and efficiency of electric motors. It is the stationary part of an electric motor that works in conjunction with the rotor to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The stator’s design and functionality are key to determining how efficiently and effectively an electric motor operates, making it an essential part of various industrial, commercial, and consumer applications.
The stator is typically made of laminated sheets of steel to minimize energy loss due to eddy currents. The windings are placed in the slots of the stator core, and their design and configuration are critical for achieving the desired motor performance, such as speed, torque, and efficiency.
The stator serves several important functions in the operation of an electric motor:
The primary function of the stator is to generate a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field. This interaction is responsible for producing the rotational force (torque) that powers the motor. In an AC motor, the stator's alternating current produces a rotating magnetic field, while in a DC motor, a constant magnetic field is generated.
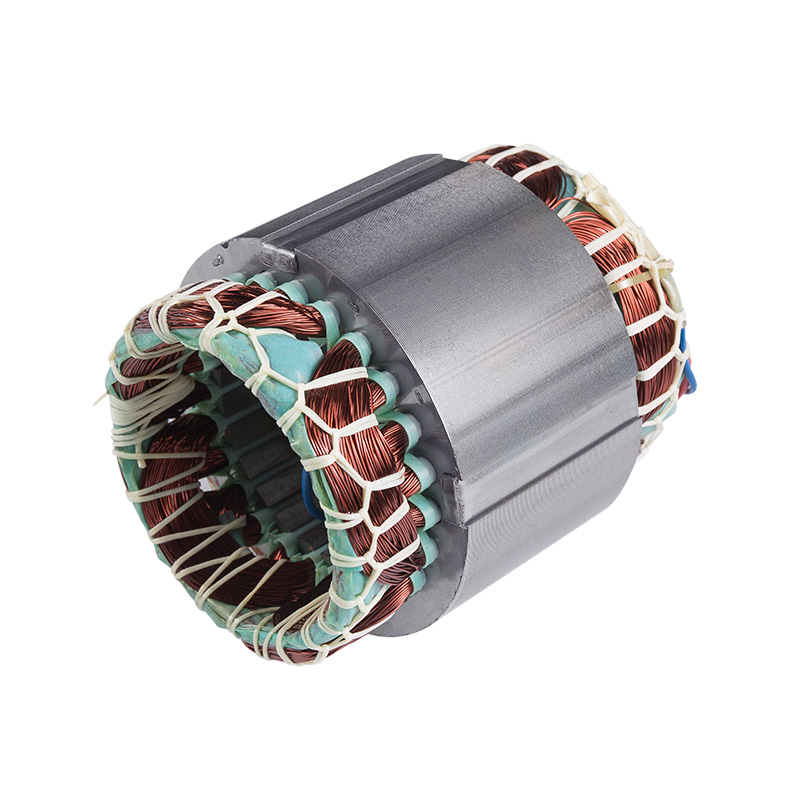

The stator is responsible for distributing electrical power to the motor windings. The windings are connected to an external power supply, which ensures that the stator receives the necessary electrical energy to generate a magnetic field.
The design and construction of the stator directly influence the efficiency and performance of the motor. Properly designed stators reduce losses, such as resistive losses (I²R losses), and minimize the effects of heat buildup during motor operation. This leads to higher efficiency, reduced power consumption, and longer motor life.
The stator also plays a role in managing heat generated during motor operation. A well-designed stator helps dissipate heat efficiently, preventing the motor from overheating and ensuring reliable, long-term performance. Heat management is particularly important in high-performance motors that operate in demanding conditions.
There are various types of electric motor stators, each designed for specific types of motors and applications. The most common types of stators are:
The squirrel cage stator is commonly found in induction motors, the most widely used type of electric motor. It features a laminated core with copper or aluminum conductors that form closed loops resembling a squirrel cage. This design provides a simple, reliable, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of industrial and household applications. The squirrel cage stator is known for its robustness and efficiency, requiring little maintenance.
Wound stators are found in wound rotor motors, which are often used in applications that require adjustable speed or high starting torque. In this design, the stator windings are made of copper wire wound around the laminated core. The wound stator is often used in large motors or special applications where more control over the motor’s performance is needed, such as in heavy-duty machinery or mining equipment.
In permanent magnet motors, the stator works in conjunction with permanent magnets placed on the rotor. This type of stator is typically found in smaller motors, including electric vehicles, home appliances, and power tools. Permanent magnet stators are known for their high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for applications where space and power consumption are critical.
The toroidal stator is used in certain high-efficiency motors, where a toroidal (doughnut-shaped) core is employed. This design reduces the amount of material needed for the stator and improves the motor’s overall efficiency. Toroidal stators are found in specialized applications such as high-performance electric vehicles and advanced robotics.
Stators are found in industrial machinery such as pumps, conveyors, compressors, and fans. The stators in these motors are designed for durability and reliability, ensuring that the machinery can operate continuously without failure.
Many household appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, rely on electric motors powered by stators. The design of the stator ensures that these appliances operate efficiently and quietly.
Electric vehicles (EVs) use high-performance motors with advanced stator designs, such as permanent magnet or squirrel cage stators, to provide efficient propulsion. The stators in EVs are designed to offer high torque and low energy consumption, helping to maximize battery life and driving range.
In renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric power generation, the stator is an essential component in the generator. The stator helps convert mechanical energy from wind or water flow into electrical energy, contributing to the overall efficiency of the energy generation process.
Stators are also used in motors found in medical equipment, such as MRI machines, ventilators, and pumps. These motors require precise control and high reliability to ensure the proper functioning of critical healthcare devices.
When designing or selecting a stator for a specific application, several factors must be considered:
The stator must be designed to handle the required power levels for the motor to function efficiently. For high-power applications, such as industrial machinery, the stator design must accommodate larger currents and higher voltages.
The design of the stator should minimize energy losses, which can be due to resistance in the windings, eddy currents, or core losses. High-efficiency stators improve the overall performance of the motor and reduce energy consumption.
The stator must be capable of dissipating heat generated during motor operation. Heat management techniques, such as using better insulation materials and improving airflow around the stator, can help prevent overheating.
The choice of materials used for the stator, such as copper for windings and silicon steel for the core, affects its performance, efficiency, and durability. Advanced materials, such as high-temperature insulation, are often used for high-performance applications.
Related Products
-

TD high efficiency and energy saving circulating pump pump shaft
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the component that connects the motor to the impelle...
See Details -

Vertical pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -

Sewage pump body
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The pump body is the outer shell of the sewage pump, with the function...
See Details -

Sewage pump bearing seat
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed inside the sewage pump unit, they support the rotor part of ...
See Details -

Sewage pump tank
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The oil in the oil chamber, in addition to lubricating the mechanical ...
See Details -

Vertical motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
A conventional fixed-speed motor whose operating speed is usually cons...
See Details -

TD horizontal high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
1.TD horizontal high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump is ...
See Details -

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

