- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Pipeline Pumps: The Backbone of Fluid Transportation Systems
Pipeline pumps are essential components in fluid transport systems, enabling the efficient movement of liquids across long distances in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and more. With their robust designs and advanced engineering, pipeline pumps ensure uninterrupted flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance system reliability.
Pipeline pumps are typically installed at pump stations along the pipeline, where they provide the necessary pressure to overcome resistance caused by friction, elevation changes, and the viscosity of the fluid being transported. Their reliability and efficiency are crucial for minimizing downtime and operational costs.
There are several types of pipeline pumps, each suited to specific applications based on the nature of the fluid and the pipeline system requirements:
Centrifugal pumps are the most commonly used type of pipeline pumps. They operate by using a rotating impeller to impart kinetic energy to the fluid, converting it into pressure energy. These pumps are ideal for transporting low-viscosity fluids like water and light oils and are widely used in water distribution and oil pipelines.
Axial flow pumps are designed for high flow rates and low-pressure applications. These pumps move fluids along the axis of the impeller, making them suitable for irrigation systems, flood control, and large-scale water transportation.
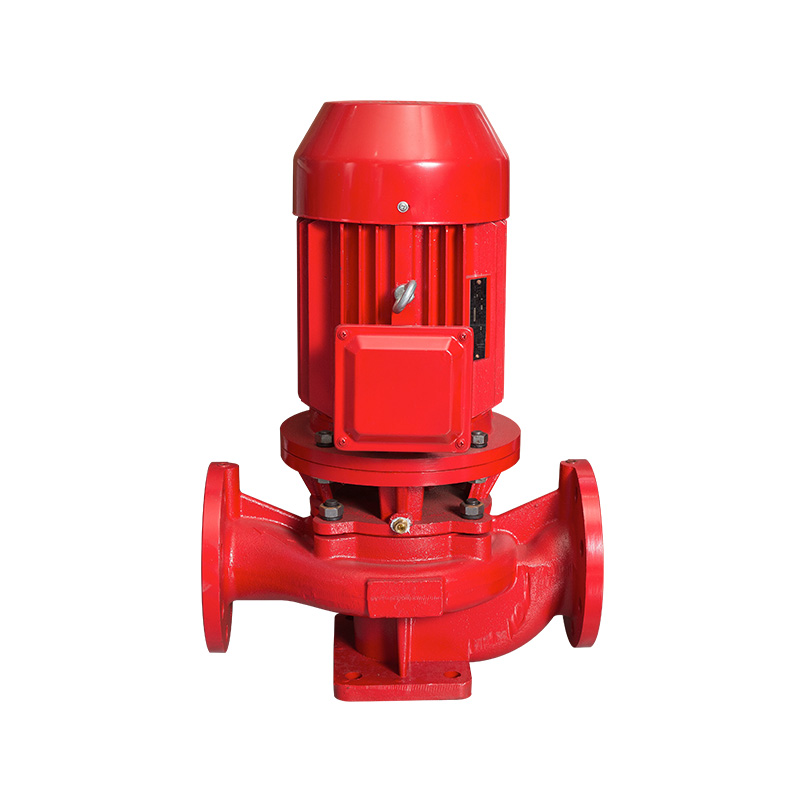

Positive displacement pumps, including gear pumps and diaphragm pumps, are used for high-pressure and low-flow applications. They are particularly effective in transporting viscous fluids or fluids containing suspended solids, such as crude oil, chemicals, or slurries.
Multistage pumps consist of multiple impellers arranged in series within a single casing. They are used in applications requiring high pressure, such as transporting water in high-rise buildings or delivering oil over long distances.
Pipeline pumps play a pivotal role in numerous industries, providing essential services that ensure the smooth operation of fluid transport systems:
Pipeline pumps are critical in transporting crude oil, refined products, and natural gas liquids over long distances. They maintain consistent flow and pressure in pipelines, reducing energy consumption and ensuring the safe delivery of hydrocarbons.
In municipal and industrial water systems, pipeline pumps facilitate the distribution of water from treatment plants to consumers. They are also used in wastewater treatment plants to handle effluent and sludge transport.
Pipeline pumps are employed in chemical plants to move acids, alkalis, solvents, and other process fluids. Their ability to handle corrosive and abrasive materials makes them indispensable in this sector.
Hygienic pipeline pumps are used to transport food-grade liquids such as milk, juice, and syrups. These pumps are designed to meet stringent sanitation standards, ensuring product safety and quality.
In mining operations, pipeline pumps transport slurries containing ores, minerals, and tailings. Their robust construction allows them to withstand the abrasive and corrosive nature of these fluids.
Pipeline pumps offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in modern fluid transport systems:
Modern pipeline pumps are engineered for energy efficiency, reducing operational costs and minimizing the environmental impact of fluid transportation.
Pipeline pumps are built for continuous operation in demanding environments, ensuring consistent performance and minimizing downtime.
With the ability to handle a wide range of fluids and pressures, pipeline pumps are suitable for diverse applications across industries.
Pipeline pumps can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different pipeline systems, from small municipal networks to large-scale industrial operations.
Choosing the right pipeline pump is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Key factors to consider include:
The viscosity, density, temperature, and chemical properties of the fluid determine the type of pump and materials of construction required.
The desired flow rate and pressure dictate the pump size and configuration. Accurate calculations ensure the pump can meet system demands without overloading.
The length, diameter, and elevation changes in the pipeline affect the pump’s performance. Detailed analysis of these factors ensures efficient operation.
Energy-efficient pumps can significantly reduce operational costs. Look for models with high-efficiency impellers and advanced control systems.
Consider the long-term maintenance requirements and total cost of ownership when selecting a pipeline pump. Pumps with easy-to-service designs and durable components offer better value over time.
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of pipeline pumps. Key maintenance practices include:
Periodically check for signs of wear, leaks, or abnormal noises. Early detection of issues prevents costly breakdowns.
Ensure bearings and other moving parts are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and extend the pump’s lifespan.
Misaligned pumps can cause excessive vibration and damage. Verify alignment during installation and after maintenance.
Use sensors and monitoring systems to track pressure, flow rate, and temperature. Sudden changes in these parameters may indicate potential problems.
Remove debris and sediment from the pump and pipeline to maintain efficiency and prevent blockages.
Related Products
-

Horizontal pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISW series single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps ar...
See Details -

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -

Pipeline pump cast iron impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The impeller refers to both the disc with moving blades, which is an i...
See Details -

Pipe pump horizontal base
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump base serves to support and secure the pump casing. Horizontal...
See Details -

Sewage pump body
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The pump body is the outer shell of the sewage pump, with the function...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump guide vane
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
A guide vane is a guiding device located at the impeller inlet that gu...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump water outlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The outlet section is the outlet part of the pump, which is responsibl...
See Details -

LG multi-stage pump seal gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The machine seal gland is a component that encloses the machine seal u...
See Details -

Vertical motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
A conventional fixed-speed motor whose operating speed is usually cons...
See Details -

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

